¶ MIC
There is a MIC on the development board at the following location
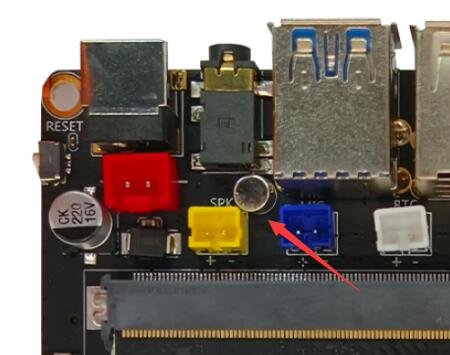
The MIC on the board is connected to the top of the RK809 sound card. The schematic is shown below

The current framework used for audio under Linux is ALSA (Advanced Linux Sound Architecture). This framework contains both kernel and application parts.
There are test programs inside alsa, such as recording with arecord. This command is used in the following way
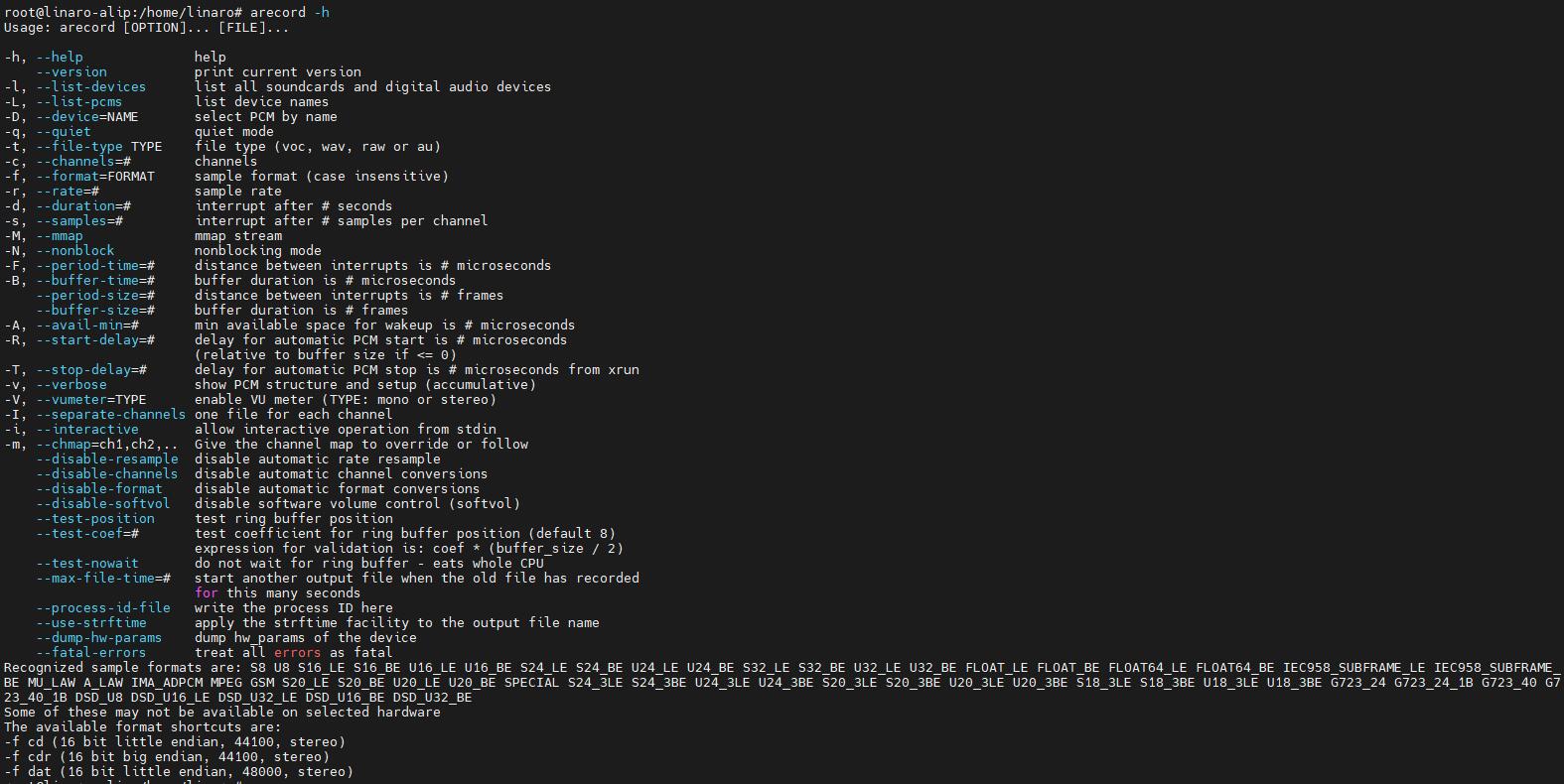
For example, the following command
arecord -D hw:0,0 --period-size=1024 --buffer-size=4096 -r 16000 -c 8 -f s32_le /tmp/r.wav
This command line means, use device 0 of sound card 0 to record, buffer size is 4096, period size is 1024, sample rate is set to 16k, use 8 channels, format is s32_le, output file is /tmp/r.wav
After executing this command, recording will start. The recorded audio format is wav, which is supported by most players.
If you use C language, you need to use the dynamic libraries on the board. These dynamic libraries and header files are needed for cross-compilation. The dynamic libraries and header files on the board can be downloaded at the following link
Then the following is a demo that can record with buffer size 4096, period size 1024, sample rate set to 16k, format S32_LE, and output file as /tmp/output.raw. The note has explained how to use the related API, you can refer to it.
#include <alsa/asoundlib.h>
#include <alsa/pcm.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define CHANNELS 2
#define FSIZE 2 * CHANNELS
#define SOUND_CARD_DEVICE "hw:0,0"
int main()
{
int fd;
int ret = 0;
char output_filename[] = "/tmp/output.raw";
// Create an output file
fd = open(output_filename, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0777);
if (fd < -1) {
printf("open file:%s fail.\n", output_filename);
exit(1);
}
snd_pcm_t *handle;
// Turn on a sound card, where the second parameter is the sound card number, which can be viewed with the cat /proc/asound/cards command
// The third parameter specifies which way to open, here CAPTURE is used
ret = snd_pcm_open(&handle, SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, SND_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_open %s fail %d\n", SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, ret);
exit(1);
}
// Initialize the snd_pcm_hw_params_t structure type parameter
snd_pcm_hw_params_t *params;
snd_pcm_hw_params_malloc(¶ms);
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_any(handle, params);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_any %s fail %d \n", SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, ret);
exit(1);
}
// Set multiplexed data output mode
// SND_PCM_ACCESS_RW_INTERLEAVED Interleaved mode means that the data of the left and right channels are crossed in each period
// SND_PCM_ACCESS_RW_NONINTERLEAVED Non-interleaved mode
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_access(handle, params, SND_PCM_ACCESS_RW_INTERLEAVED);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_access %s fail %d \n",SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, ret);
exit(1);
}
// Set the sampling format, that is, the arrangement of the data in the buf
// SND_PCM_FORMAT_S16_LE 16-bit small end
// SND_PCM_FORMAT_S16_BE 16-bit big end
// SND_PCM_FORMAT_S32_LE 32-bit small end
// SND_PCM_FORMAT_S32_BE 32-bit big end
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_format(handle, params, SND_PCM_FORMAT_S32_LE);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_format %s fail %d \n",SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, ret);
exit(1);
}
// Set the number of sound channels
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_channels(handle, params, CHANNELS);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_channels %s fail %d \n",SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, ret);
exit(1);
}
unsigned int val = 48000;
int dir;
// Set the sampling rate
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_rate_near(handle, params, &val, &dir);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_rate_near %s %d HZ fail %d \n", SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, val, ret);
exit(1);
}
// There are two ways to set the buffer, either by size or by time
#if 0
// Set buffer time and cycle time
buffer_time = 50000;//us
period_time = 26315;
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_buffer_time_near(handle, params, &buffer_time, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_buffer_time_near %s %d fail %d \n", SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, buffer_time, ret);
exit(1);
}
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_time_near(handle, params, &period_time, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_time_near %s %d fail %d \n", SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, period_time, ret);
exit(1);
}
#else
snd_pcm_uframes_t buffer_size = 4096;
snd_pcm_uframes_t period_size = 1024;
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_size_near(handle, params, &period_size, &dir);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_size_near %s %d fail %d \n", SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, period_size, ret);
exit(1);
}
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_buffer_size_near(handle, params, &buffer_size);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params_set_buffer_size_near %s %d fail %d \n", SOUND_CARD_DEVICE, buffer_size, ret);
exit(1);
}
#endif
// Let these parameters act on the PCM device
ret = snd_pcm_hw_params(handle, params);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("snd_pcm_hw_params %s fail\n",SOUND_CARD_DEVICE);
exit(1);
}
// Get the real cycle buf size of the current sound card again
snd_pcm_uframes_t frames;
snd_pcm_hw_params_get_period_size(params, &frames, &dir);
printf("period_size:%ld\n", frames);
int size;
// 1 frame = channels * sample_size.
size = frames * FSIZE; /* 2 bytes/sample, 1 channels */
printf("size:%d\n", size);
char *buffer;
buffer = (char *)malloc(size);
while (1) {
ret = snd_pcm_readi(handle, buffer, frames);
if (ret == -EPIPE) {
// EPIPE means overrun
fprintf(stderr, "overrun occurred\n");
ret = snd_pcm_prepare(handle);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("Failed to recover form overrun");
break;
}
} else if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "error from read: %s\n", snd_strerror(ret));
break;
} else if (ret != (int)frames) {
// fprintf(stderr, "short read, read %d frames\n", ret);
usleep(1);
}
ret = write(fd, buffer, size);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("fail to write to audio file\n");
}
fflush(stdout);
}
close(fd);
snd_pcm_drain(handle);
snd_pcm_close(handle);
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(params);
free(buffer);
return 0;
}
The compile-time command is
aarch64-linux-gcc mic_record.c -L./usr/lib/ -lasound -I./usr/include/ -o mic_record
Note that the compiler should use prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-buildroot-9.3.0-2020.03-x86_64_aarch64-rockchip-linux-gnu under sdk, so that it is consistent with the alsa library that comes with the board