¶ Linux Source code compilation
¶ 1 Compilation environment
Two compilation schemes are provided here. If you want to compile directly, choose scheme 1. If you want to compile with docker, choose scheme 2.
Notes:
1. SDK uses cross-compilation, so you should use SDK on an X86_64 computer, and do not download SDK to the board.
2. Please use Ubuntu20.04/Ubuntu22.04 (real machine or docker container) as the compilation environment. If you use other versions, compilation errors may occur.
3. Do not store or decompress SDK in virtual machine shared folders or non-English directories.
4. Please use ordinary users throughout the process of obtaining and compiling SDK. Root permissions are not allowed or required (unless apt is required to install software)
¶ 2 Decompress source code
Preparations, select configuration according to your own situation
Download the source code from the download page and put it in the x86 Ubuntu host or virtual machine.
Download, click to jump
mkdir YY3588_Debian12
tar zxf yy3588_linux6.1_release_v0.0_20250429_sdk.tar.gz -C YY3588_Debian12
.repo/repo/repo sync -l
¶ 3 Compilation method
¶ Software dependencies
Install dependencies required for source code compilation
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install git ssh make gcc libssl-dev liblz4-tool expect g++ patchelf chrpath gawk texinfo chrpath diffstat binfmt-support qemu-user-static live-build bison flex fakeroot cmake gcc-multilib g++-multilib python2 unzip device-tree-compiler ncurses-dev
./yy3588-build.sh
The size of the complete firmware obtained by the complete compilation is more than 4G. Burning the complete firmware takes a long time, which is not conducive to debugging of drivers and other programs. Here is a step-by-step compilation, which requires
- Compile
ubootseparately
cd u-boot
./make.sh rk3588
- Compile
kernelseparately
cd kernel
make CROSS_COMPILE=../prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 rockchip_linux_defconfig rk3588_linux.config
make CROSS_COMPILE=../prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 rk3588s-yyt.img
- Compile separately
reocvery
./build.sh recovery
- Package complete firmware
./build.sh firmware
./build.sh updateimg
¶ Software dependencies
Install dependencies required for source code compilation
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
sudo apt update
apt-cache policy docker-ce
sudo apt install docker-ce
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo reboot
sudo systemctl status docker
./docker/docker-rm.sh
./docker/docker-start.sh
./yy3588-build.sh
- Open docker compilation environment
./docker/docker-rm.sh
./docker/docker-start.sh
- Separate compilation
uboot
cd u-boot
./make.sh rk3588
- Separate compilation
kernel
cd kernel
make CROSS_COMPILE=../prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu-ARCH=arm64 rockchip_linux_defconfig rk3588_linux.config
make CROSS_COMPILE=../prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu-ARCH=arm64 rk3588s-yyt.img
- Compile separately
reocvery
./build.sh recovery
- Package complete firmware
./build.sh firmware
./build.sh updateimg
¶ Android source code compilation
¶ 1 Compilation environment
Two compilation schemes are provided here. If you want to compile directly, choose scheme 1. If you want to compile with docker, choose scheme 2.
Notes:
1. SDK uses cross-compilation, so use SDK on X86_64 computer, do not download SDK to the board.
2. Please use Ubuntu20.04/Ubuntu22.04 (real machine or docker container) as the compilation environment. If you use other versions, compilation errors may occur.
3. Do not store or decompress SDK in virtual machine shared folders or non-English directories.
4. Obtain and compile SDK. Please use ordinary users throughout the process. Root permissions are not allowed or required (unless apt is required to install software).
¶ 2 Preface
¶ 2.1 Hardware requirements
Compiling Android requires high machine configuration:
¶ 2.2 Increase swap memory (optional)
If you are using 16g physical memory, to complete the compilation of Android14 source, you need to add 16G swap memory. The following are the steps to increase swap memory.
- Create a file to be used as a swap file:
sudo fallocate -l 16G /swapfile
- Set the file permissions to 600 to prevent regular users from reading and writing to this file:
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
- Create a Linux swap area on this file:
sudo mkswap /swapfile
- Activate the swap area by running the following command:
sudo swapon /swapfile
- Use swapon command to verify that the swap area is activated
sudo swapon --show
- Make the setting permanent
sudo vim /etc/fstab
## Add the following content
/swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0
¶ 3 Unzip the source code
Download the source code from the download page and put it in the x86 Ubuntu host or virtual machine.
Download, click to jump
Steps to unzip the source code:
mkdir YY3588_Android14
cat yy3588_android14.0_release_v0.0_20250514_sdk.tgz* | tar zxf - -C YY3588_Android14
cd YY3588_Android14
.repo/repo/repo sync -l
¶ 4 Compilation method
Before compiling the source code, you need to install a series of environment dependencies.
¶ Install dependencies.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install git gnupg flex bison gperf libsdl1.2-dev \
libesd-java libwxgtk3.0-dev squashfs-tools build-essential zip curl \
libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev pngcrush schedtool libxml2 libxml2-utils \
xsltproc lzop libc6-dev schedtool g++-multilib lib32z1-dev lib32ncurses5-dev \
lib32readline-dev gcc-multilib libswitch-perl libssl-dev unzip zip device-tree-compiler \
liblz4-tool python-pyelftools python3-pyelftools -y
Complete compilation is to merge a series of partition firmwares such as uboot and boot partition firmware into a complete firmware. Burning the complete firmware is simpler than burning the partition.
source build/envsetup.sh
lunch rk3588_u-userdebug
./build.sh -UKAu
Partition compilation is to compile each partition source code separately into partition firmware. The partition firmware is much smaller than the complete firmware. In driver debugging, the corresponding partition firmware is burned separately without burning other partitions. Greatly improve the speed of burning firmware and debugging speed.
- Export Android compilation environment
source build/envsetup.sh
lunch rk3588_u-userdebug
- Compile
ubootseparately
./build.sh -U
- Compile
kernelseparately
./build.sh -K
- Compile
androidseparately
./build.sh -A
- Package into complete firmware
./build.sh -u
A series of environment dependencies need to be installed before compiling the source code.
¶ Software dependencies that need to be installed.
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
sudo apt update
apt-cache policy docker-ce
sudo apt install docker-ce
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo reboot
sudo systemctl status docker
¶ Complete compilation
Complete compilation is to merge a series of partition firmware such as uboot and boot partition firmware into a complete firmware. Burning the complete firmware is simpler than burning the partition.
./docker/docker-rm.sh
./docker/docker-start.sh
source build/envsetup.sh
lunch rk3588_u-userdebug
./build.sh -UKAu
¶ Step-by-step compilation
Partition compilation is to compile each partition source code separately into partition firmware. The partition firmware is much smaller than the complete firmware. In driver debugging, the corresponding partition firmware is burned separately without burning other partitions. Greatly improve the speed of burning firmware and debugging.
- Start the docker compilation environment
./docker/docker-rm.sh
./docker/docker-start.sh
- Compile
ubootseparately
./build.sh -U
- Compile
kernelseparately
./build.sh -K
- Compile
androidseparately
./build.sh -A
- Package into complete firmware
./build.sh -u
¶ Ubuntu 22.04 Source Code Usage Tutorial
¶ Source code compilation
- Download source code
- Split the source code into compressed files and perform MD5 verification to ensure that the downloaded source code is complete. Enter the following command in the X86 Ubuntu system for verification
md5sum -c yy3588_linux6.1_ubuntu22.04_release_v1.0_20251210_sdk.tar.md5sum
- No problem with verification, start unpacking the source code
mkdir yy3588Ubuntu && tar -zxf yy3588_linux6.1_ubuntu22.04_release_v1.0_20251210_sdk.tar -C yy3588Ubuntu
.repo/repo/repo sync -l
- After extracting the source code, compilation begins. There are two compilation methods provided here: one is to compile directly, and the other is to create a Docker container for compilation
- Install and compile environment
sudo apt-get install git gnupg flex bison gperf libsdl1.2-dev \
libesd-java libwxgtk3.0-dev squashfs-tools build-essential zip curl \
libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev pngcrush schedtool libxml2 libxml2-utils \
xsltproc lzop libc6-dev schedtool g++-multilib lib32z1-dev lib32ncurses5-dev \
lib32readline-dev gcc-multilib libswitch-perl libssl-dev unzip zip device-tree-compiler \
liblz4-tool python-pyelftools python3-pyelftools -y
- Compile source code
./yy3588-build.sh
- Generate the firmware path in the rockdev directory and burn the rockdev/update.img file.
- Install Docker
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
sudo apt update
apt-cache policy docker-ce
sudo apt install docker-ce
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo reboot
sudo systemctl status docker
- Start Docker
./docker/docker-start.sh
- Compile source code
./yy3588-build.sh
- Generate the firmware path in the rockdev directory and burn the rockdev/update.img file.
¶ Overlayfs file system usage
¶ Introduction to the directory structure of Overlays
This source code uses the Overlayfs file system to divide the root file system of Ubuntu firmware into three parts: rootfs, oe, and userdata, which are stored on the corresponding partitions of rootfs, oe, and userdata. Rootfs and OEM are maintained by the manufacturer and should not be touched by users. Users only need to modify in the corresponding position of userdata. After system startup, the contents of the three partitions will be merged and mounted to the userdata partition. Files with the same name in the same path will be overwritten, and different files in the same path will be merged into the same directory.
Introduction to the directory structure of Overlays in this Ubuntu source code
The path corresponding to OEM is device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/oem/normal As shown in the figure below:
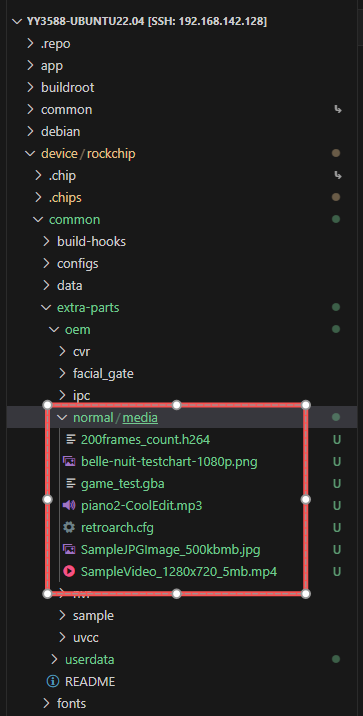
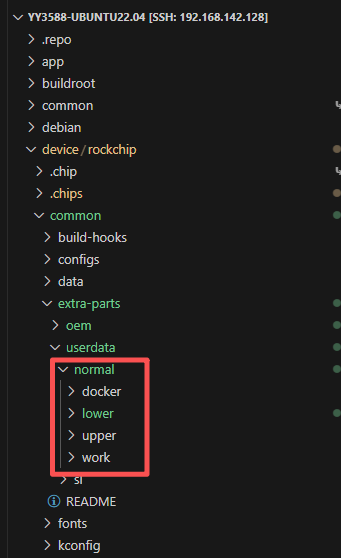
userdata对应的路径: device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/, As shown in the figure below:
The path corresponding to rootfs is: rockdev/rootfs.img
The coverage relationship is as follows:
-
device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/Files with the same name in the same path will be overwrittendevice/rockchip/common/extra-parts/oem/normalThe files under the same path will be merged into the same directory. -
device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/oem/normalFiles with the same name in the same path will be overwrittenrockdev/rootfs.imgThe files under the same path will be merged into the same directory.
¶ Overlays operation
- modify file
Copy a file to be modified to device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/The corresponding location in the directory, and then modify it.
For example, modifying the media/recoarch.cfg file
cp device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/oem/normal/media/retroarch.cfg device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/media/retroarch.cfg
# Modify the content of retro arch.cfg
vim device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/media/retroarch.cfg
# Compile source code
rm -fr output
./yy3588-build.sh
Burn the firmware, and after the system is up, check if the content of/media/recoarch.cfg has changed.
- Create a file
If the file in a certain path under the Ubuntu root file system does not exist, the user only needs to create the file directly or copy the file to the specified path. For example, a hello.sh script needs to be built-in in the/bin/directory of the Ubuntu root file system.
Operate in the source code directory:
# If the directory under device/dockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/usr/bin does not exist, create the corresponding directory
mkdir -p device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/usr/bin
# Create corresponding files
echo 'echo "hello world!!!"' > device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/usr/bin/hello.sh
# Add executable permissions
chmod +x device/rockchip/common/extra-parts/userdata/normal/usr/bin/hello.sh
# Compile source code
rm -fr output
./yy3588-build.sh
Burn the firmware, and after the system is up, you can see the /bin/hello.sh file. Run /bin/hello.sh to see the effect.
- Delete file
Overlayfs file deletion creates a whiteout file to mask underlying files with the same name, and this file is not visible in the Overlayfs merge layer, so users cannot see the deleted file or directory. The whiteout file is not a regular file, but a character device with primary and secondary device numbers of 0.
mknod <filename> c 0 0
For example, if we want to delete media/game_test.gba from the OEM partition, it is not recommended to delete it directly. Instead, we can create a whiteout file named game_test.gba in the lower directory of the userdata partition.
# Mount userdata.img
mkdir rockdev/tmp
sudo mount rockdev/userdata.img rockdev/tmp
# Create a whiteout file named game_test.gba.
sudo mknod rockdev/tmp/media/game_test.gba c 0 0
sudo umount rockdev/tmp
# Compile source code
./yy3588-build.sh
Burn the firmware and check if/media/game_test.gba still exists after the system is up.
- move file
It involves two operations: creating files and deleting files. I won't elaborate on it here.