¶ GPIO
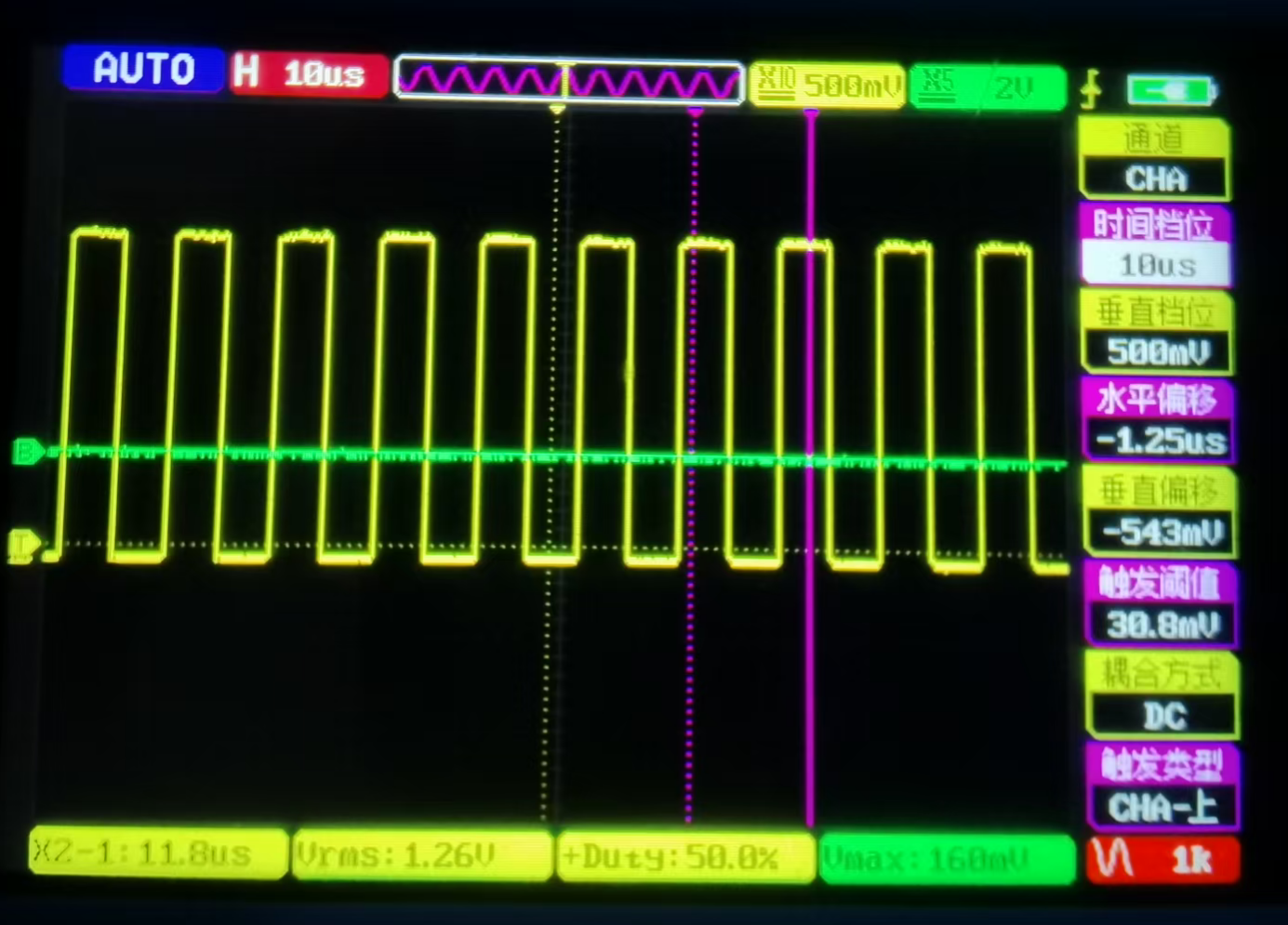
GPIO, the full name of which is General-Purpose Input/Output, is a type of general-purpose pin that can be dynamically configured and controlled during software operation. On the RK platform, except for some pins with specific purposes (such as DDR, MIPI, etc.), for other pins, if multiplexing is not configured, the default multiplexing state is GPIO. The GPIO driver of RK provides the standard GPIO interface under Linux. Under Linux, there is a set of user-space sysfs nodes that operate on GPIO. The programming of GPIO at the application layer is mainly achieved by operating these nodes.
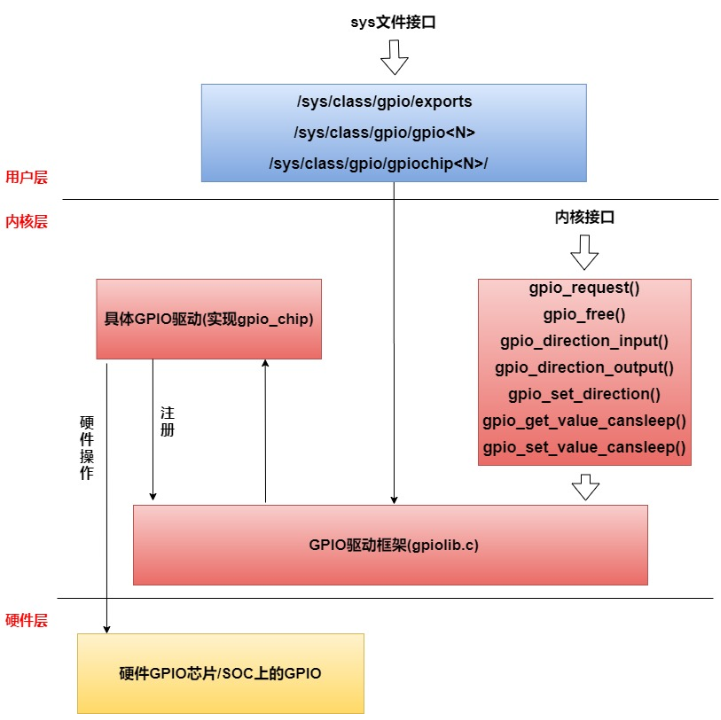
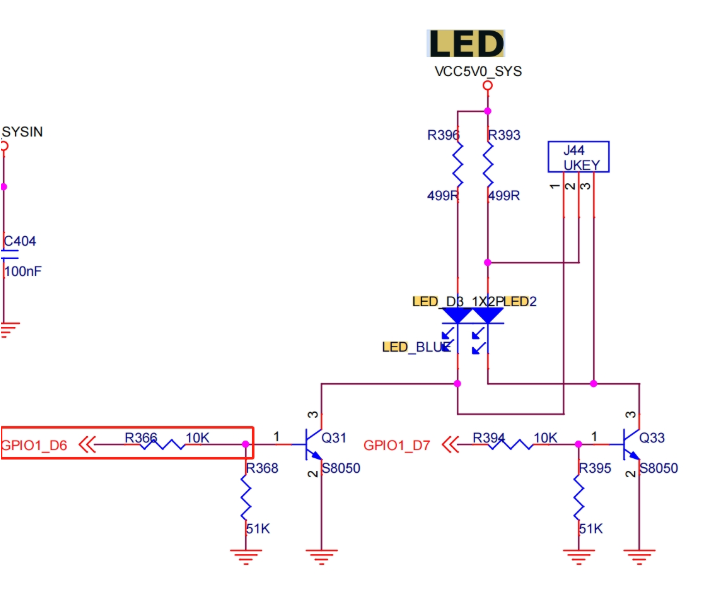
The following takes the operation of GPIO1_D6 as an example for introduction. The location of this GPIO is as follows
Under the universal Linux framework, all GPIOs are numbered with numbers. For the chips of the RK platform, the calculation method for their numbering is
(gpio controller number -0)*32+(port number - 'A')*8+ index number
The controller number of GPIO1_D6 is 1, the port number is D, and the index number is 6, so the number is
(1-0) * 32 + 3 * 8 + 6 = 62
¶ Command line operation of GPIO
- Set GPIO 62 to user mode operation
echo 62 > /sys/class/gpio/export
- Set GPIO 101 as the output
echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio62/direction
- Set the level when GPIO 62 is the output
- High level
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio62/value
- Low level
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio62/value
- Set GPIO 62 as the input
echo in > /sys/class/gpio/gpio62/direction
- In the case where GPIO 101 is the input, read its level. 1 is high and 0 is low
cat sys/class/gpio/gpio62/value
- Cancel the user mode operation of GPIO 101
echo 62 > /sys/class/gpio/unexport
- Execution effect

¶ USB3.0
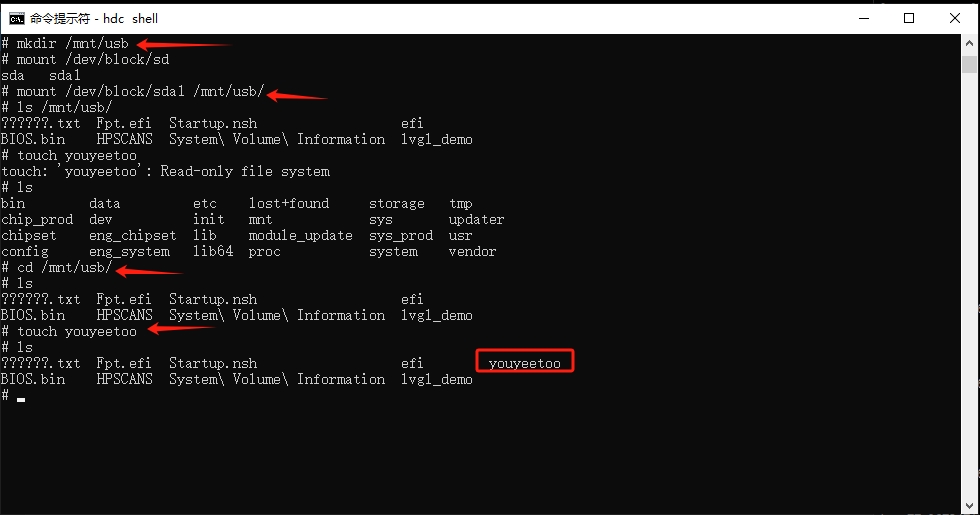
- Mount the USB flash drive to the system via USB as follows:
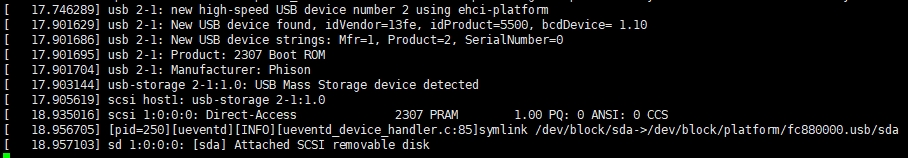
# mkdir /mnt/usb
# mount /dev/block/sda1 /mnt/usb
# cd /mnt/usb
# ls
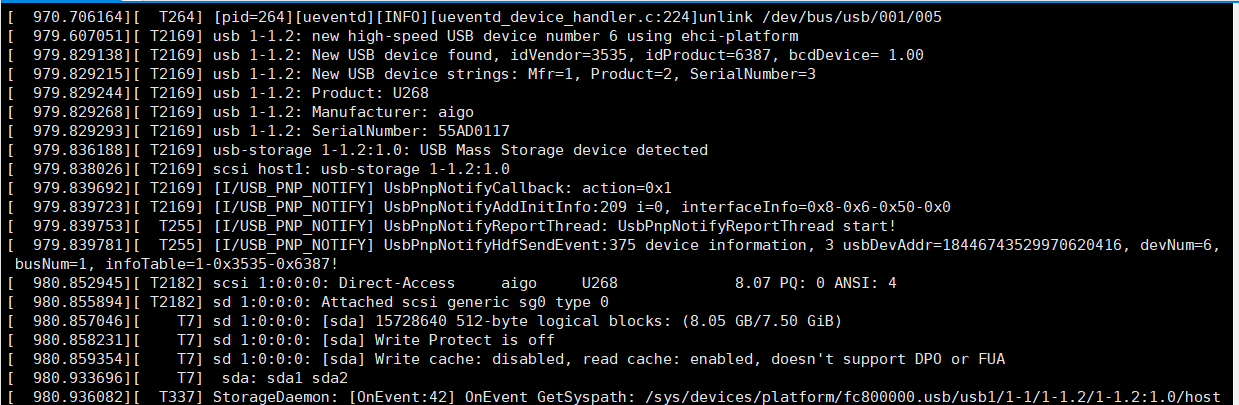
- Execution effect
¶ USB2.0
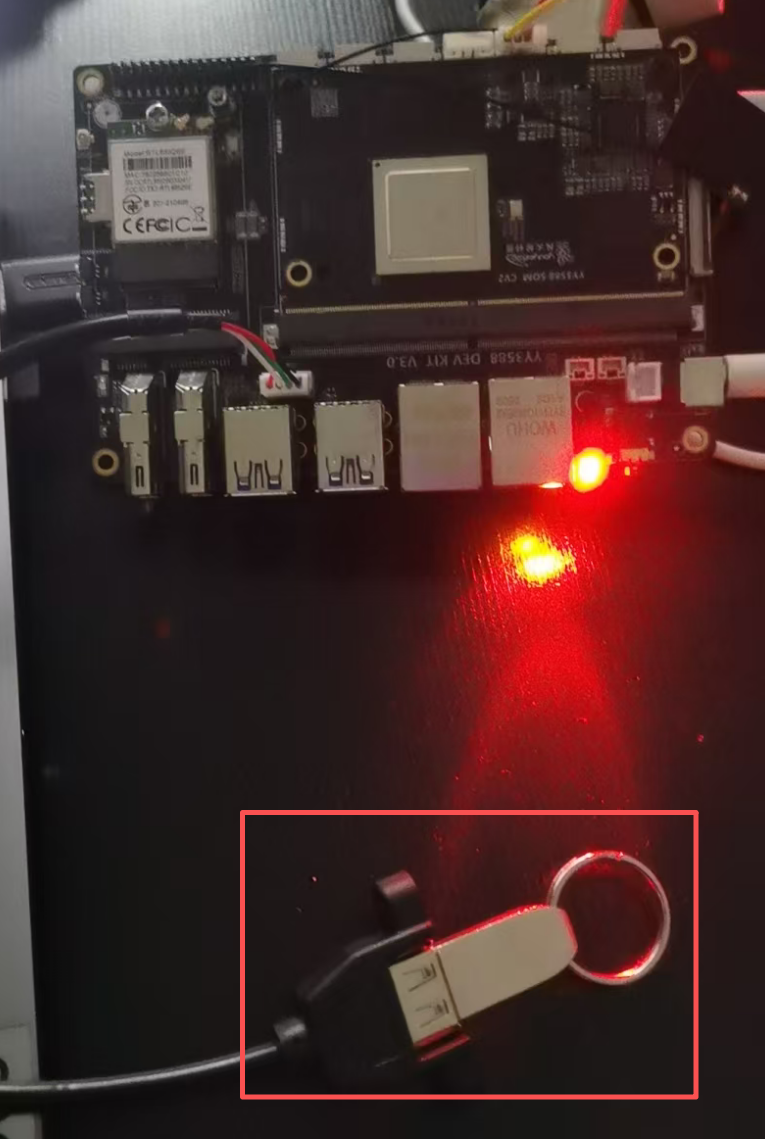

- Mount the USB flash drive to the system via USB as follows:
# mkdir /mnt/usb
# mount /dev/block/sda1 /mnt/usb
# cd /mnt/usb
# ls
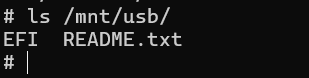
- Execution effect
¶ UART
Rockchip UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is based on the 16550A serial port standard. The kernel uses the 8250 serial port universal driver, thus it can support standard serial port programming under Linux.
-
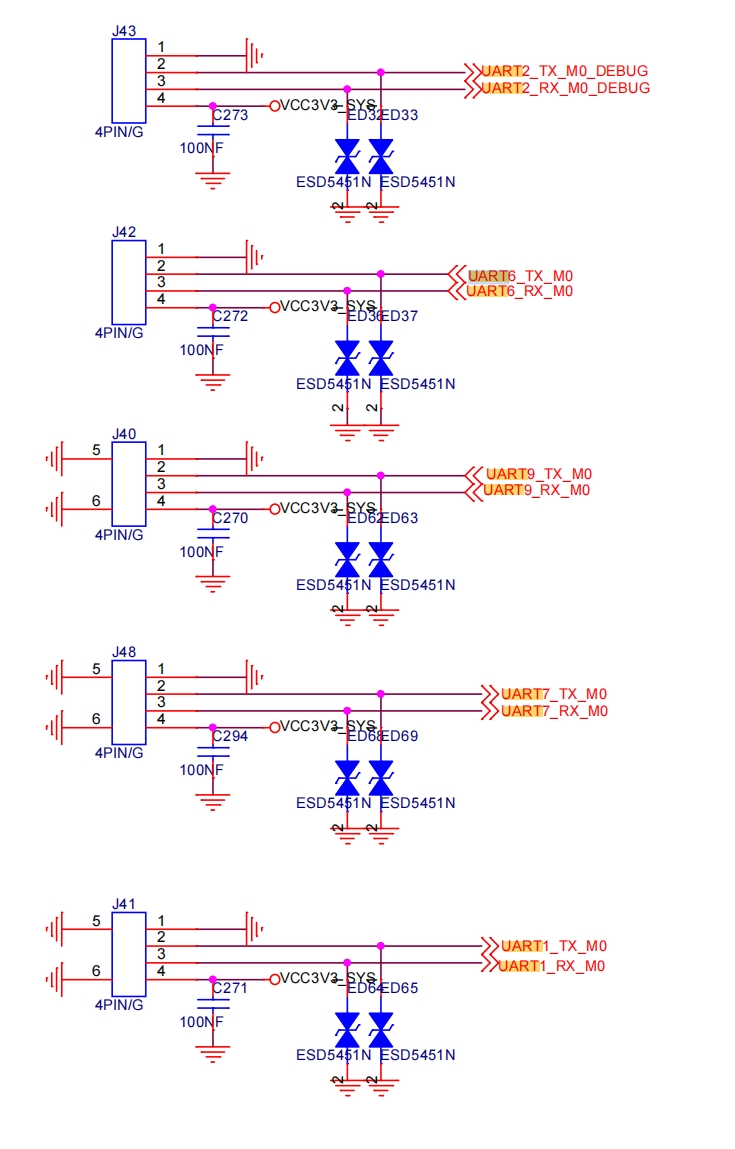
The serial numbers of these three universal serial ports are 6, 7, and 9 respectively (if serial port No. 9 multiplexes i2c, it should not be used anymore). Under Linux, the corresponding device nodes are /dev/ttyS6 and /dev/ttyS7 (/dev/ttyS9) respectively. The following takes ttyS7 as an example to introduce its usage. The other several serial ports are similar.
-
In terms of hardware, a serial port module is used to connect the TX and RX of ttyS7, with a baud rate of 9600. The wiring diagram is as follows:
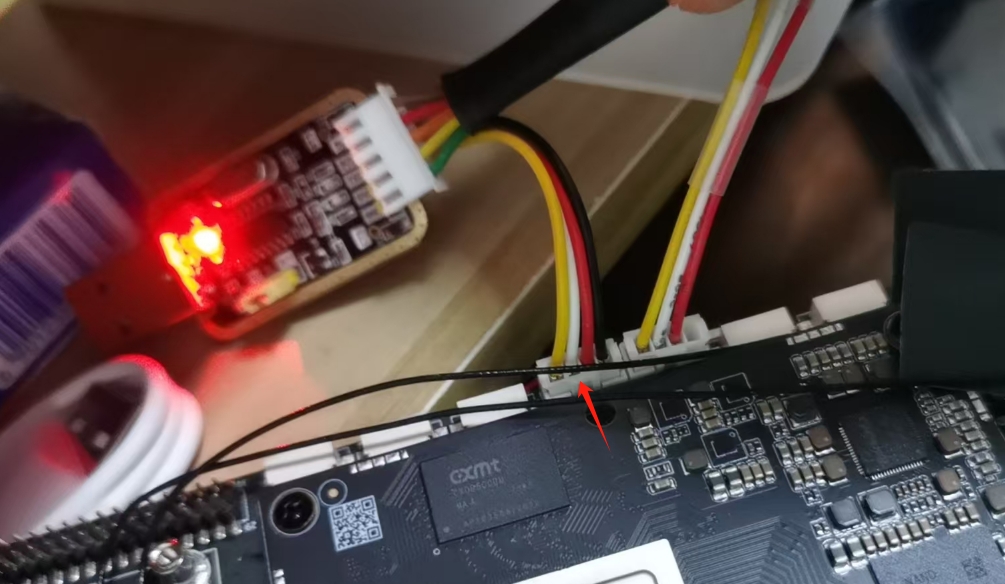
- Send data
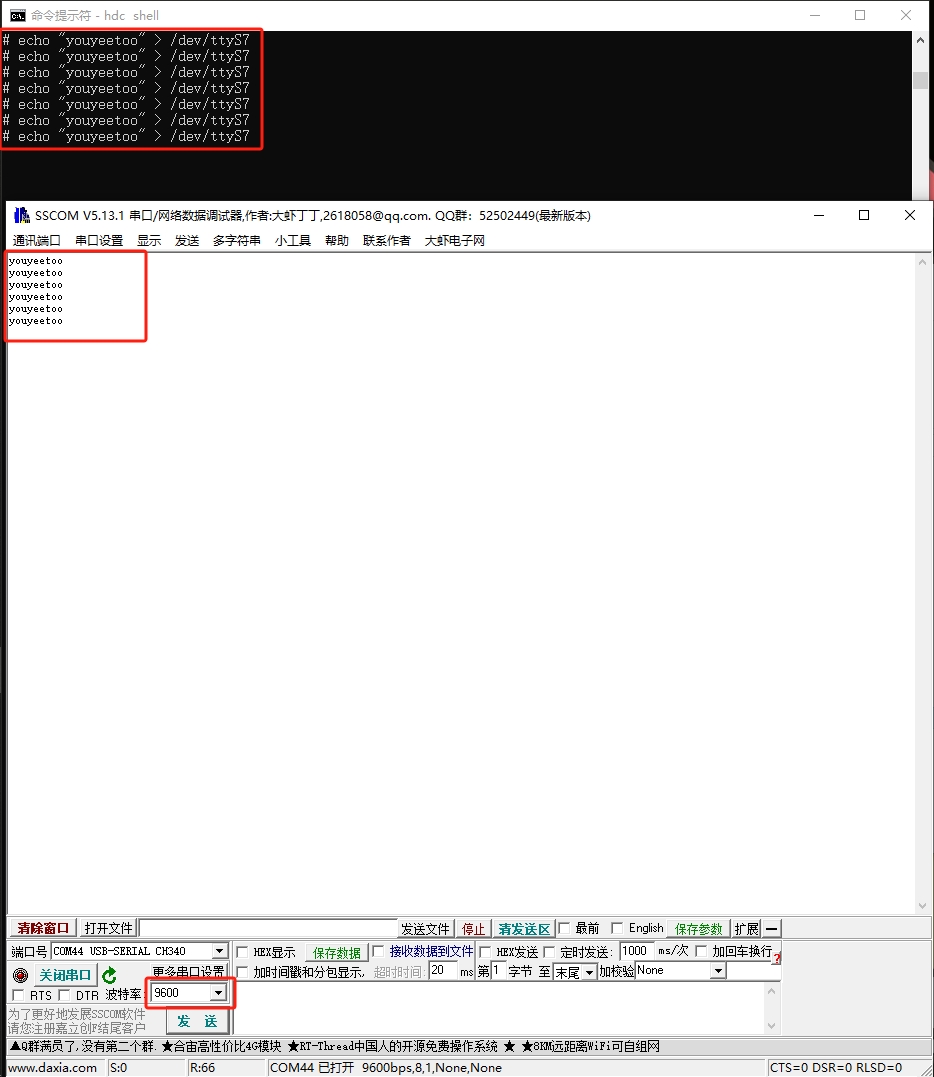
echo "youyeetoo" > /dev/ttyS6
Execution effect
¶ I2C
- The I2C-Tools tool is an open-source device specifically designed for debugging I2C. It can obtain mounted devices and their addresses, and also read and write i2c device registers.
- Usage method of i2c-tools:
- View all i2c buses.
# i2cdetect -l
- View the functions supported by the specified i2c bus
# i2cdetect -F 2
- Check the devices mounted on the 2C2-2 bus
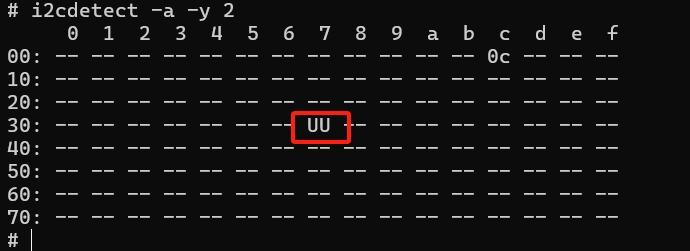
# i2cdetect -a -y 2
The appearance of 'UU' in the figure indicates that there is a device at that address and the device matches the driver
The appearance of "--" in the picture indicates that there is no device at this address
The appearance of "numbers" in the figure indicates that there is a device at this address, but the device does not match the driver
- Connect the board to the camera and check if it has been detected

¶ CAN
CAN (Controller Area Network) is an efficient and reliable communication protocol used for real-time control and data exchange. It was originally developed by the German company BOSCH and has now become an international standard ISO 11898. The CAN bus adopts a multi-master competitive bus structure, supporting multiple nodes to simultaneously send and receive data. It features error detection and automatic retransmission functions, which can effectively enhance the reliability and real-time performance of the system. CAN is widely used in fields such as automobiles, industrial automation, and robotics, and is an indispensable part of modern electronic systems.
- The use of can
- Query the current network device
ifconfig -a
- Set can
canconfig can0 down
canconfig can0 type can bitrate 1000000 dbitrate 3000000 on
canconfig can0 up
canconfig can0 start
//or
canconfig can0 down
canconfig can0 type can bitrate 1000000 loopback on
canconfig can0 up
canconfig can0 start
- can transceiver
cansend can0 -v -i 12 13 12 12
candump can0
¶ PWM
The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) function is very common in embedded systems. It is a highly effective technology that uses the digital output of a microprocessor to control analog circuits and is widely applied in many fields ranging from measurement and communication to power control and conversion.
Rockchip PWM can support standard PWM interface programming under Linux.
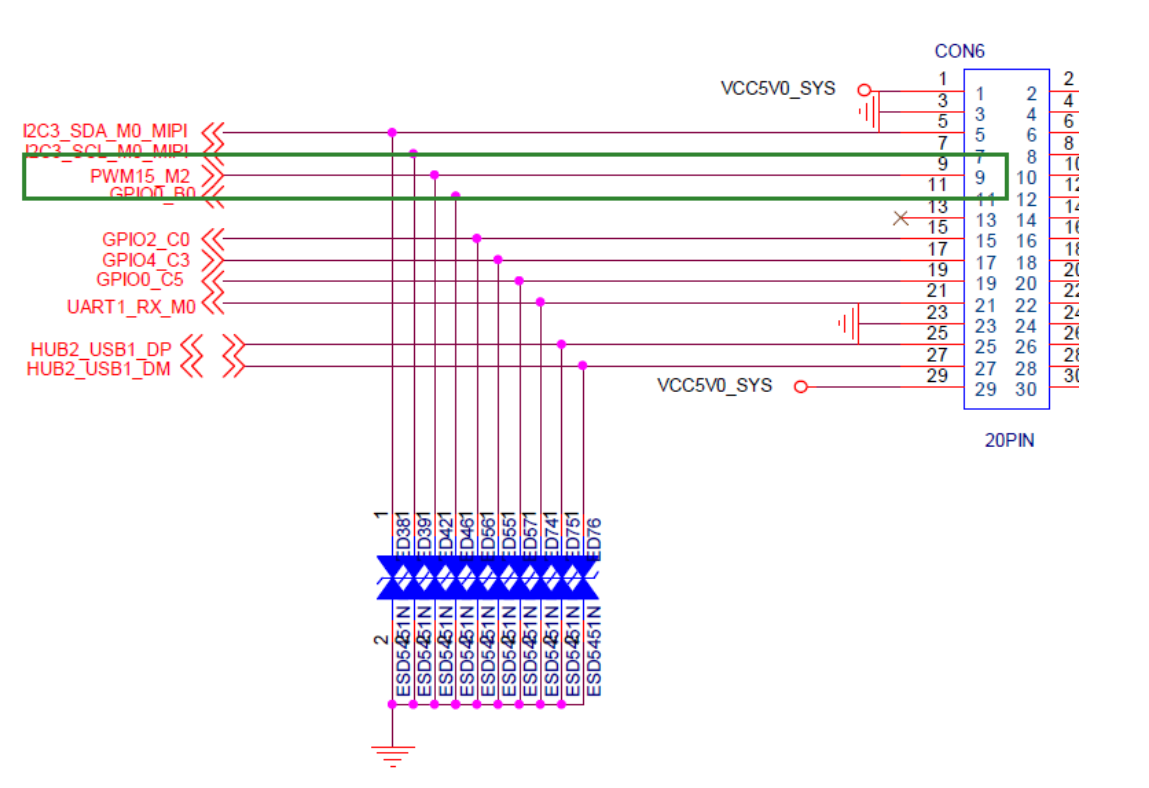
One PWM is led out from the board for custom purposes, and the rest is PWM for screen backlighting, which has been exclusively occupied by other drivers and cannot be used for other functions.
- The following command can be used to view which pwm devices are on the board
# find /sys -name "*pwmchip*"
/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip2
/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0
/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip1
/sys/devices/platform/fd8b0020.pwm/pwm/pwmchip0
/sys/devices/platform/febf0030.pwm/pwm/pwmchip2
/sys/devices/platform/fd8b0030.pwm/pwm/pwmchip1
By querying the device tree, it can be known that febf0030 are respectively the starting addresses of the registers of pwm15, so pwmchip3 is a node of pwm15.
- Test verification
# cd /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip2/
# echo 0 > export
# cd pwm0
# echo 10000 > period
# echo 5000 > duty_cycle
# echo 1 > enable