¶ GPIO Programming
Linux GPIO can be controlled via the sysfs interface by navigating to the /sys/class/gpio directory.
export: Used to export a GPIO pin with a specified number. Before using a GPIO pin, it needs to be exported. Once successfully exported, it can be used.
unexport: Used to remove an exported GPIO pin. After using a GPIO pin, we need to remove the exported pin. Writing the specified number into the export file will export the GPIO pin with that number, and after a successful export, a corresponding gpioX (X indicates the GPIO number) will be created under the /sys/class/gpio directory.
direction: Configures the GPIO pin as input or output. This file is both readable and writable; reading it shows whether the GPIO is currently set as input or output, and writing to it sets the GPIO as input or output. The acceptable values for read or write operations are "out" (output mode) and "in" (input mode).
value: When the GPIO is configured as output, writing "0" to the value file sets the GPIO output to low, while writing "1" sets it to high. In input mode, reading the value file retrieves the current input level of the GPIO pin.
active_low: This attribute file is used to control polarity and is both readable and writable.
edge: Controls the interrupt trigger mode. This file is readable and writable. Before configuring the interrupt trigger mode of a GPIO pin, it should be set to input mode:
Non-interrupt pin: echo "none" > edge
Rising edge trigger: echo "rising" > edge
Falling edge trigger: echo "falling" > edge
Both edge trigger: echo "both" > edge
The Rockchip GPIO corresponding user-space GPIO numbers are shown in the table below.
| GPIO | GPIO Number |
|---|---|
| GPIO0_B0 | 8 |
| GPIO2_C0 | 80 |
| GPIO4_C3 | 147 |
| GPIO0_C5 | 21 |
| GPIO4_C4 | 148 |
| GPIO4_C5 | 149 |
| GPIO2_B2 | 74 |
| GPIO2_B1 | 73 |
¶ Configure GPIO output
cd /sys/class/gpio/
# Change the file owner to youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo export
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo unexport
# Using GPIO0_B0 as an example to operate GPIO output, other GPIO operations can be exported according to the correspondence in the previous table.
# Export GPIO0_B0
echo 8 > export
# Change the file owner to youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/direction
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/value
cd gpio8
# Set Output
echo out > direction
# Output high level
echo 1 > value
# Output low level
echo 0 > value
# Unexport GPIO pin
cd ..
echo 8 > unexport
vim gpio_output.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
static char gpio_path[32];
static int gpio_config(const char *attr, const char *val)
{
char file_path[64];
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, attr);
fd = open(file_path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
len = strlen(val);
if (len != write(fd, val, len)) {
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //Close file
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd;
int len;
/* Validate parameters */
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <gpio> <value>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* Check if the specified GPIO number is exported */
sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]);
//If the directory does not exist, it needs to be exported.
if (access(gpio_path, F_OK)) {
fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
len = strlen(argv[1]);
//Export GPIO
if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len)) {
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //Close file
}
/* Configure as output mode */
if (gpio_config("direction", "out")) return -1;
/* Polarity Settings */
if (gpio_config("active_low", "0")) return -1;
/* Control GPIO output high and low levels */
if (gpio_config("value", argv[2])) return -1;
close(fd);
/* Exit program */
return 0;
}
gcc gpio_output.c -o gpio_output
# Output high level
sudo ./gpio_output 8 1
# Output low level
sudo ./gpio_output 8 0
¶ Configure GPIO input
cd /sys/class/gpio/
# Change the file owner to youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo export
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo unexport
# Using GPIO0_B0 as an example to operate GPIO output, other GPIO operations can be exported according to the corresponding relationships in the previous table.
# Export GPIO0_B0
echo 8 > export
# Change the file owner to youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/direction
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/value
cd gpio8
# Set Input
echo in > direction
# Check GPIO level
cat value
# Remove exported GPIO pin
cd ..
echo 8 > unexport
vim gpio_input.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
static char gpio_path[32];
static int gpio_config(const char *attr, const char *val)
{
char file_path[64];
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, attr);
if (0 > (fd = open(file_path, O_WRONLY))) {
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
len = strlen(val);
if (len != write(fd, val, len)) {
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //Close file
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char file_path[64];
char val;
int fd;
int len;
/* Validate parameters */
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <gpio>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* Check if the specified GPIO number is exported */
sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]);
// If the directory does not exist, it needs to be exported
if (access(gpio_path, F_OK)) {
if ((fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY)) < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
len = strlen(argv[1]);
// Export GPIO
if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len)) {
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //Close file
}
/* Configure as input mode */
if (gpio_config("direction", "in")) return -1;
/* Polarity Settings */
if (gpio_config("active_low", "0")) return -1;
/* Configured for non-interrupt mode */
if (gpio_config("edge", "none")) return -1;
/* Read GPIO voltage level */
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, "value");
if ((fd = open(file_path, O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
if (read(fd, &val, 1) < 0) {
perror("read error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
printf("value: %c\n", val);
/* Exit program */
close(fd);
return 0;
}
Compile and run, read the GPIO pin level
gcc gpio_input.c -o gpio_input
sudo ./gpio_input 8
¶ Configure GPIO interrupt
vim gpio_irq.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <poll.h>
static char gpio_path[32];
static int gpio_config(const char *attr, const char *val)
{
char file_path[64];
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, attr);
fd = open(file_path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
len = strlen(val);
if (len != write(fd, val, len)) {
perror("write error");
return -1;
}
close(fd); //Close file
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct pollfd pfd;
char file_path[64];
int ret;
char val;
int len;
int fd;
/* Validate parameters */
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <gpio>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* Check if the specified GPIO number is exported */
sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]);
// If the directory does not exist, it needs to be exported
if (access(gpio_path, F_OK)) {
fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
len = strlen(argv[1]);
// Export GPIO
if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len)) {
perror("write error");
return -1;
}
close(fd); //Close file
}
/* Configure as input mode */
if (gpio_config("direction", "in")) return -1;
/* Polarity Settings */
if (gpio_config("active_low", "0")) return -1;
/* Configure interrupt trigger mode: rising edge and falling edge */
if (gpio_config("edge", "both")) return -1;
/* Open the value attribute file */
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, "value");
pfd.fd = open(file_path, O_RDONLY);
if (pfd.fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
/* Call poll */
pfd.events = POLLPRI; //Only care about high-priority data being readable (interrupt)
read(pfd.fd, &val, 1); // First, read once to clear the status
while (1) {
ret = poll(&pfd, 1, -1); //Call poll
if (ret < 0) {
perror("poll error");
return -1;
} else if (ret == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "poll timeout.\n");
continue;
} else {
/* Check if high-priority data is readable */
if(pfd.revents & POLLPRI) {
if (lseek(pfd.fd, 0, SEEK_SET) < 0) { //Move the read position to the head
perror("lseek error");
return -1;
}
if (read(pfd.fd, &val, 1) < 0) {
perror("read error");
return -1;
}
printf("GPIO Interrupt Trigger <value=%c>\n", val);
}
}
}
/* Exit program */
return 0;
}
Compile and run
gcc gpio_irq.c -o gpio_irq
sudo ./gpio_irq
¶ UART Programming
Serial communication is an important device communication method that transmits data between devices through serial communication. In Linux systems, serial devices are abstracted as special files located in the/dev directory. Common serial device files include/dev/ttyS0,/dev/ttyS1 (traditional serial ports),/dev/ttyUSB0,/dev/ttyACM0 (USB to serial devices). The following core parameters need to be configured in serial communication.
The core parameters of serial communication include:
- Baud Rate: Data transmission rate, commonly including 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, etc
- Data Bits: The actual number of data bits contained in each data frame, typically 5-8 bits
- Stop Bits: The number of bits used to indicate the end of a data frame, typically 1 or 2 bits
- Parity Bit: Used for simple error detection, it can be None, Odd, or Even
- Flow Control: Used to control the data transmission rate, it can be None, XON/XOFF, or RTS/CTS
The YY3588 development board provides a total of 4 UART for customers to use, registered as ttyS1, ttyS6, ttyS7, and ttyS9. Please refer to the schematic diagram for the corresponding hardware locations. The serial port can be configured using either shell mode or programming language read-write mode. This article only introduces shell mode and C language mode.
- Check the serial port configuration on the development board. By default, the baud rate of the serial port is 9600.
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 -a
- Connect the serial port
Connect the TX of the board to the RX of the serial module, connect the RX of the board to the TX of the serial module, and then connect the GND of the board to the GND of the serial module. Then connect the serial module to the computer.
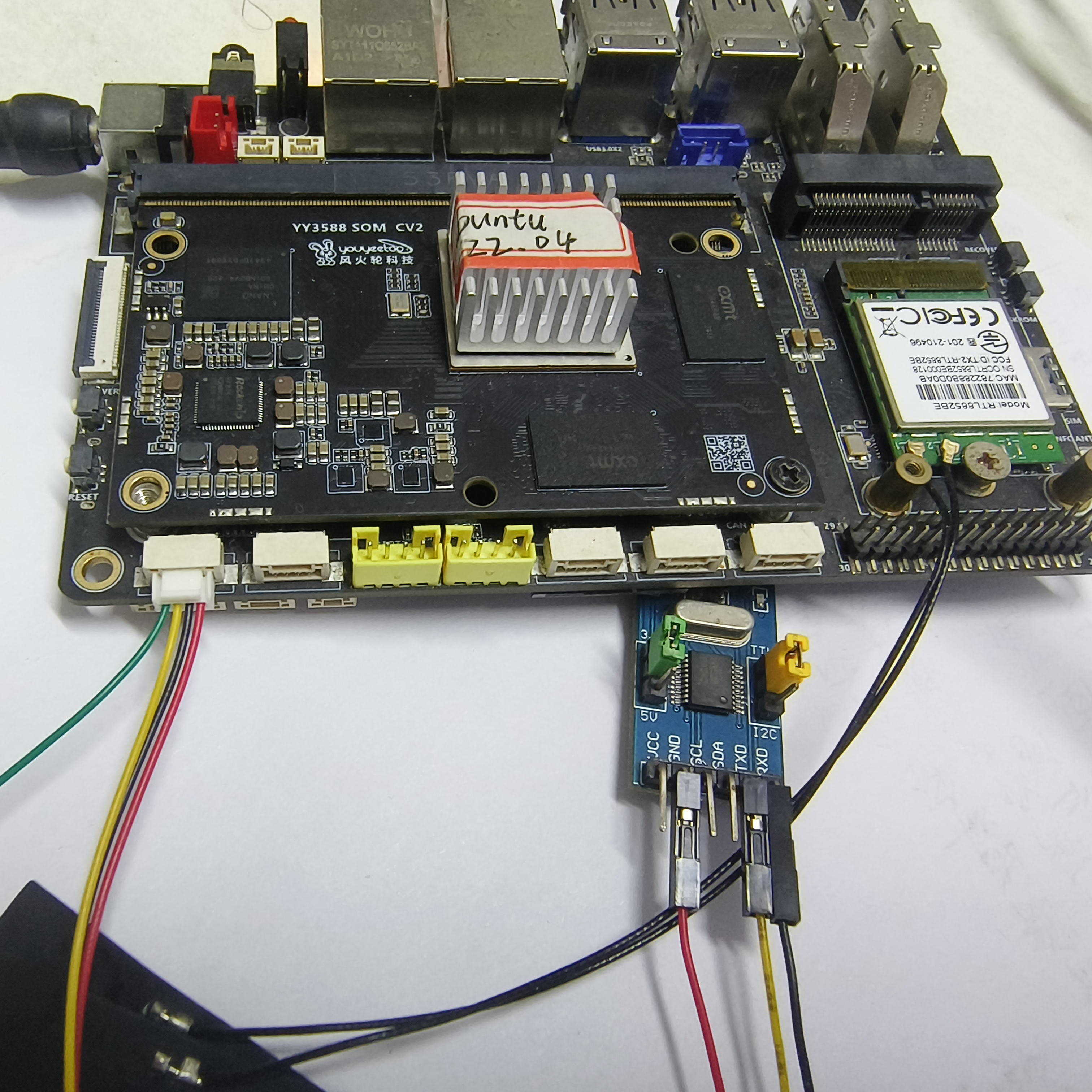
-
Open the serial port software on the computer and configure the default 9600 in the serial port software to complete communication.
-
Enter the following command on the development board to receive the serial port data sent over
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS1
cat /dev/ttyS1
- The development board sends serial data commands
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS1
echo "Serial information to be sent" > /dev/ttyS1
If you need to modify the baud rate, data bits, and other configurations, execute the following command.
#Set the baud rate of/dev/ttyS1 serial port to 115200
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 speed 115200
#Set data bits, such as setting 8-bit data bit parameters as cs8 and 7-bit data bits as cs7
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 cs8
#The stop bit is used to indicate the end of a character transfer. Usually 1 or 2 stop bits are used. One stop bit parameter is cstopb, and two stop bits are - csstopb
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 cstopb
#Set odd verification:
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 parenb parodd
#Set as even check:
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 parenb -parodd
#Turn off verification:
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 -parenb
- The serial port software on the computer should also be set to match the serial port parameters on the development board to complete serial communication.

C language serial port programming in Linux environment usually includes the following basic steps:
- Open serial device: Use the open() function to open the serial device file
- Configure serial port parameters: Use the tcgetattr() and tcsetattr() functions to configure serial port parameters
- Read and write data: Use the read() and writable functions for data transmission and reception
- Close serial device: Use the close() function to close the serial device
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int configure_serial_port(const char *device, int baud_rate)
{
int serial_port;
serial_port = open(device, O_RDWR);
if (serial_port < 0) {
printf("Error %i opening %s: %s\n", errno, device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
struct termios tty;
memset(&tty, 0, sizeof tty);
if (tcgetattr(serial_port, &tty) != 0) {
printf("Error %i from tcgetattr: %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return -1;
}
// 设置波特率
cfsetospeed(&tty, baud_rate);
cfsetispeed(&tty, baud_rate);
// 设置8N1模式:8位数据位,无校验位,1位停止位
tty.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; // 无校验位
tty.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; // 1位停止位
tty.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; // 清除数据位设置
tty.c_cflag |= CS8; // 8位数据位
// 禁用硬件流控制
tty.c_cflag &= ~CRTSCTS;
// 启用接收,忽略调制解调器控制线
tty.c_cflag |= CREAD | CLOCAL;
// 禁用软件流控制
tty.c_iflag &= ~(IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
// 原始输入模式
tty.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
// 原始输出模式
tty.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
// 设置超时和最小读取字符数
tty.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; // 至少读取1个字符
tty.c_cc[VTIME] = 1; // 等待字符的超时时间为0.1秒
// 保存设置
if (tcsetattr(serial_port, TCSANOW, &tty) != 0) {
printf("Error %i from tcsetattr: %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return -1;
}
return serial_port;
}
int main()
{
const char *device = "/dev/ttyS1";
int baud_rate = B9600;
// 配置串口
int serial_port = configure_serial_port(device, baud_rate);
if (serial_port < 0) {
return 1;
}
// 写入数据
const char *message = "Hello, Serial Port!";
ssize_t bytes_written = write(serial_port, message, strlen(message));
if (bytes_written < 0) {
printf("Error writing to serial port: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return 1;
}
printf("Written %zd bytes: %s\n", bytes_written, message);
// 读取数据
unsigned char buffer[256];
ssize_t bytes_read = read(serial_port, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read < 0) {
printf("Error reading from serial port: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return 1;
}
// 确保字符串以null结尾
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0';
printf("Read %zd bytes: %s\n", bytes_read, buffer);
// 关闭串口
close(serial_port);
return 0;
}
Compile and run the C program, and connect the serial port according to the shell method.
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS1
gcc serial.c -o serial
sudo ./serial
¶ I2C Programming
In the Linux environment, there are various tools available to assist users in interacting with I2C devices. The most commonly used tools are the command-line tools provided in the i2c tools package, including i2cdetect, i2cset, and i2cget.
- Install i2c tools tool
sudo apt-get install i2c-tools
- Check the devices mounted on the i2c6 bus
sudo i2cdetect -y 6
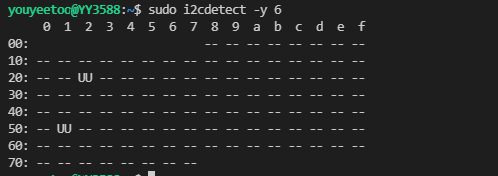
-
There is a device at address 0x51 in the above figure, which is HYM8563 or RTC. This article uses RTC as an example to explain i2c reading and writing.
-
Read command format
sudo i2cget -y -f 'i2c Bus' 'number slave address' 'register'
- Description of the month/century register (address 07H) bit of HYM8563
| Tag | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | C | Century bit: C=0 specifies the century as 20XX; C=1 specifies the century as 19XX, and "XX" is the value in the year register |
| 6,5 | - | Invalid |
| 4~0 | Month | represents the current month value in BCD format, with values ranging from 01 to 12 |
- Description of the year register (address 08H) bit of HYM8563
| Tag | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | Year | Represents the current year value in BCD format, ranging from 00 to 99 |
The command to read the month/century register and year register is as follows
The command to read the month/century register and year register is as follows
# Read month/century register
sudo i2cget -y -f 6 0x51 0x07
# Read the year register
sudo i2cget -y -f 6 0x51 0x08
# Check RTC time
sudo hwclock -r
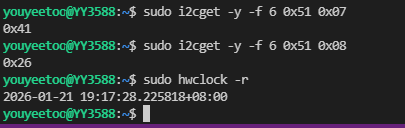
Read the month/century register value as 0x41, convert it to binary as 01000001, and obtain C=0, which means the century is 20, the month is January, and the year register value is 0x26. Convert it to BCD code format as 26. The year and month read out is 2026-01, which is consistent with the year and month read out by the hwclock command.
- Write command format
sudo i2cset -y -f 'i2c Bus' 'number slave address' 'register' 'value'
If the RTC clock year and month is set to 2027-02, the command is as follows
# Set month/century register
sudo i2cset -y -f 6 0x51 0x07 0x42
# Set year register
sudo i2cset -y -f 6 0x51 0x08 0x27
# Check RTC time
sudo hwclock -r
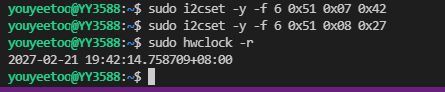
This C program uses RTC as an example to perform I2C read and write. See shell mode for related slave addresses and register introductions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <linux/i2c-dev.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
/* The device node of the I2C controller corresponding to RTC */
#define RTC_DEVICE "/dev/i2c-6"
/* RTC I2C device address */
#define RTC_ADDR 0x51
int i2c_write(int fd, unsigned char dev_addr, unsigned char reg_addr, unsigned char* data_buf, int len)
{
int ret;
unsigned char msg_buf[9];
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data data;
struct i2c_msg messages;
msg_buf[0] = reg_addr;
if (len < 9) {
memcpy((void *) &msg_buf[1], data_buf, len);
} else {
printf("This function supports up to 8 bytes at a time !!!\n");
return -1;
}
messages.addr = dev_addr;
messages.flags = 0;
messages.len = len + 1;
messages.buf = msg_buf;
data.msgs = &messages;
data.nmsgs = 1;
if(ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, &data) < 0) {
printf("I2C_RDWR err \n");
return -1;
}
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
int i2c_read(int fd, unsigned char dev_addr, unsigned char reg_addr, unsigned char* data_buf, int len)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data data;
struct i2c_msg messages[2];
messages[0].addr = dev_addr;
messages[0].flags = 0;
messages[0].len = 1;
messages[0].buf = ®_addr;
messages[1].addr = dev_addr;
messages[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;
messages[1].len = len;
messages[1].buf = data_buf;
data.msgs = messages;
data.nmsgs = 2;
if(ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, &data) < 0) {
printf("I2C_RDWR err \n");
return -1;
}
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int fd;
unsigned char reg=0x07;
unsigned char rd_buf[2] = {0};
unsigned char wr_buf[2] = {0x42, 0x27};
fd = open(RTC_DEVICE, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("open"RTC_DEVICE"failed \n");
return -1;
}
i2c_read(fd, RTC_ADDR, reg, rd_buf, 2);
printf("read reg(0x07): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[0]);
printf("read reg(0x08): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[1]);
i2c_write(fd, RTC_ADDR, reg, wr_buf, 2);
i2c_read(fd, RTC_ADDR, reg, rd_buf, 2);
printf("write reg(0x07): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[0]);
printf("write reg(0x08): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[1]);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
Compile and run the C program.
gcc i2c_test.c -o i2c_test
sudo ./i2c_test
¶ CAN
- Install CAN tool
sudo apt-get install can-utils
- View CAN nodes
ifconfig -a
- Set CAN node
sudo ifconfig can0 down
sudo ip link set can0 type can bitrate 500000 triple-sampling on
# If there is no CAN device for testing, you can use the following command to set CAN as a loopback test.
sudo ip link set can0 type can loopback on
sudo ifconfig can0 up
- View the status of CAN nodes
sudo ip -details link show can0
- Open two terminal interfaces (one for viewing and one for sending)
- Send and receive CAN messages
sudo cansend can0 123#000102030405060708
- Receive messages
sudo candump can0
CAN communication process
- Open the socket
- Specify communication equipment
- Bind the communication device and socket
- Set filtering rules
- Receive the data sent in a loop (verify if an error frame has been received, verify frame format, verify frame type, print data)
- Close the socket
- Example of CAN sending application program
/* 1. Message sending program */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/can.h>
#include <linux/can/raw.h>
int main()
{
int s, nbytes;
struct sockaddr_can addr;
struct ifreq ifr;
struct can_frame frame[2] = {{0}};
s = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW); // Create socket
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, "can0" );
ioctl(s, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr); //Specify can0 device
addr.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr.can_ifindex = ifr.ifr_ifindex;
bind(s, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)); //Bind the socket to can0
//Disable filtering rules. This process does not receive messages and is only responsible for sending them
setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, NULL, 0);
//Generate two messages
frame[0].can_id = 0x11;
frame[0]. can_dlc = 1;
frame[0].data[0] = 'Y';
frame[1].can_id = 0x22;
frame[1]. can_dlc = 1;
frame[1].data[0] = 'N';
//Cycle sending two messages
while(1)
{
nbytes = write(s, &frame[0], sizeof(frame[0])); //Send frame [0]
if(nbytes != sizeof(frame[0]))
{
printf("Send Error frame[0]\n!");
break; //Sending error, exit
}
sleep(1);
nbytes = write(s, &frame[1], sizeof(frame[1])); //Send frame[1]
if(nbytes != sizeof(frame[0]))
{
printf("Send Error frame[1]\n!");
break;
}
sleep(1);
}
close(s);
return 0;
}
- Example of CAN receiving program
/* 2. Message filtering and receiving program */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/can.h>
#include <linux/can/raw.h>
int main()
{
int s, nbytes;
struct sockaddr_can addr;
struct ifreq ifr;
struct can_frame frame;
struct can_filter rfilter[1];
s = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW); //Create socket
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, "can0" );
ioctl(s, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr); //Specify can0 device
addr.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr.can_ifindex = ifr.ifr_ifindex;
bind(s, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)); //Bind the socket to can0
//Define the receiving rule to only receive messages with an identifier equal to 0x11
rfilter[0].can_id = 0x11;
rfilter[0].can_mask = CAN_SFF_MASK;
//Set filtering rules
setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, &rfilter, sizeof(rfilter));
while(1)
{
nbytes = read(s, &frame, sizeof(frame)); //Receive message
//Explicit Message
if(nbytes > 0)
{
printf(“ID=0x%X DLC=%d data[0]=0x%X\n”, frame.can_id,
frame.can_dlc, frame.data[0]);
}
}
close(s);
return 0;
}
¶ OpenCV
OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library) is an open-source software library for computer vision and machine learning. Composed of a series of C functions and a small number of C++classes, it also provides interfaces for languages such as Python, Java, MATLAB, etc.
- Before programming with OpenCV, it is necessary to first understand the current built-in OpenCV version, which can be queried using the following command
pkg-config --modversion opencv4
The default built-in version of this system is 4.13.0.
- Create project directory
mkdir OpenCV_Demo
cd OpenCV_Demo
mkdir build image src
- Create source file
- CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project( OpenCV_Demo )
find_package( OpenCV REQUIRED )
include_directories( ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
add_executable( image_demo src/image_demo.cpp )
add_executable( video_demo src/video_demo.cpp )
add_executable( camera_demo src/camera_demo.cpp )
target_link_libraries( image_demo ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
target_link_libraries( video_demo ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
target_link_libraries( camera_demo ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
- src/image_demo.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// Read image
cv::Mat image = cv::imread("../image/image.png");
// Confirm successful image reading
if(image.empty()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open image file." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Control photo scale
resize(image, image, cv::Size(1280, 720));
// display image
cv::imshow("Image with Box", image);
// Waiting button
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
- src/video_demo.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
int main() {
// Open video file
VideoCapture cap("../image/video.mp4");
// Check if the video has been successfully opened
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
std::cout << "Error opening video stream or file" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Loop reading video frames
while (true) {
Mat frame;
// Read the current frame
cap >> frame;
// Check if the frame has been successfully read
if (frame.empty())
break;
// Display the current frame
imshow("Frame", frame);
// Press the Esc key to exit the loop
if (waitKey(25) == 27)
break;
}
// Release VideoCapture object and all windows
cap.release();
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
- src/camera_demo.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main() {
// Open default camera
VideoCapture cap(41);
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
cout << "Unable to open camera!" << endl;
return -1;
}
namedWindow("camera", WINDOW_NORMAL);
while (true) {
Mat frame;
cap >> frame;
// Display video frames
imshow("camera", frame);
// Press the spacebar to take a photo
if (waitKey(30) == ' ')
{
// generate file name
time_t now = time(NULL);
tm *ltm = localtime(&now);
string filename = to_string(ltm->tm_year + 1900) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_mon + 1) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_mday) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_hour) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_min) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_sec) + ".jpg";
// Save image
imwrite(filename, frame);
cout << "Saved photos:" << filename << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
-
Place your videos and images in the 'image' directory and name them 'image.png' and 'video.mp4' respectively. The camera demo here uses a USB camera as an example.
-
compile
cd build
cmake ..
make
- execute program
./image_demo
./video_demo
./camera_demo

¶ MPP
- View MPP and VPU library versions
pkg-config --modversion rockchip_mpp
pkg-config --modversion rockchip_vpu
- Download Rockchip MPP source code library
git clone https://github.com/rockchip-linux/mpp.git
-
In the downloaded MPP directory, there is the test directory, which contains some official MPP calling routines. Users can refer to the test directory and doc documentation directory.
-
Here, refer to the test/mpi_dec_test.c routine for writing
vim mpp_dec_test.c
Specify the header files in the official routine and link libraries during gcc compilation.
The source code is as follows
#define MODULE_TAG "mpp_dec_test"
#include <string.h>
#include <rockchip/rk_mpi.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_mem.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_env.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_time.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_common.h>
#include <rockchip/mpi_dec_utils.h>
typedef struct {
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd;
MppCtx ctx;
MppApi *mpi;
RK_U32 quiet;
/* end of stream flag when set quit the loop */
RK_U32 loop_end;
/* input and output */
DecBufMgr buf_mgr;
MppBufferGroup frm_grp;
MppPacket packet;
MppFrame frame;
FILE *fp_output;
RK_S32 frame_count;
RK_S32 frame_num;
RK_S64 first_pkt;
RK_S64 first_frm;
size_t max_usage;
float frame_rate;
RK_S64 elapsed_time;
RK_S64 delay;
FILE *fp_verify;
FrmCrc checkcrc;
} MpiDecLoopData;
static int dec_simple(MpiDecLoopData *data)
{
RK_U32 pkt_done = 0;
RK_U32 pkt_eos = 0;
MPP_RET ret = MPP_OK;
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd = data->cmd;
MppCtx ctx = data->ctx;
MppApi *mpi = data->mpi;
MppPacket packet = data->packet;
FileBufSlot *slot = NULL;
RK_U32 quiet = data->quiet;
FrmCrc *checkcrc = &data->checkcrc;
// when packet size is valid read the input binary file
ret = reader_read(cmd->reader, &slot);
mpp_assert(ret == MPP_OK);
mpp_assert(slot);
pkt_eos = slot->eos;
if (pkt_eos) {
if (data->frame_num < 0 || data->frame_num > data->frame_count) {
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p loop again\n", ctx);
reader_rewind(cmd->reader);
pkt_eos = 0;
} else {
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p found last packet\n", ctx);
data->loop_end = 1;
}
}
mpp_packet_set_data(packet, slot->data);
mpp_packet_set_size(packet, slot->size);
mpp_packet_set_pos(packet, slot->data);
mpp_packet_set_length(packet, slot->size);
// setup eos flag
if (pkt_eos)
mpp_packet_set_eos(packet);
do {
RK_U32 frm_eos = 0;
RK_S32 times = 30;
// send the packet first if packet is not done
if (!pkt_done) {
ret = mpi->decode_put_packet(ctx, packet);
if (MPP_OK == ret) {
pkt_done = 1;
if (!data->first_pkt)
data->first_pkt = mpp_time();
}
}
// then get all available frame and release
do {
RK_S32 get_frm = 0;
MppFrame frame = NULL;
try_again:
ret = mpi->decode_get_frame(ctx, &frame);
if (MPP_ERR_TIMEOUT == ret) {
if (times > 0) {
times--;
msleep(1);
goto try_again;
}
mpp_err("%p decode_get_frame failed too much time\n", ctx);
}
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p decode_get_frame failed ret %d\n", ret, ctx);
break;
}
if (frame) {
if (mpp_frame_get_info_change(frame)) {
RK_U32 width = mpp_frame_get_width(frame);
RK_U32 height = mpp_frame_get_height(frame);
RK_U32 hor_stride = mpp_frame_get_hor_stride(frame);
RK_U32 ver_stride = mpp_frame_get_ver_stride(frame);
RK_U32 buf_size = mpp_frame_get_buf_size(frame);
MppBufferGroup grp = NULL;
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p decode_get_frame get info changed found\n", ctx);
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p decoder require buffer w:h [%d:%d] stride [%d:%d] buf_size %d",
ctx, width, height, hor_stride, ver_stride, buf_size);
if (MPP_FRAME_FMT_IS_FBC(cmd->format)) {
MppFrame frm = NULL;
mpp_frame_init(&frm);
mpp_frame_set_width(frm, width);
mpp_frame_set_height(frm, height);
mpp_frame_set_fmt(frm, cmd->format);
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_FRAME_INFO, frm);
mpp_frame_deinit(&frm);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("set fbc frame info failed\n");
break;
}
}
grp = dec_buf_mgr_setup(data->buf_mgr, buf_size, 24, cmd->buf_mode);
/* Set buffer to mpp decoder */
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_EXT_BUF_GROUP, grp);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p set buffer group failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
break;
}
data->frm_grp = grp;
/*
* All buffer group config done. Set info change ready to let
* decoder continue decoding
*/
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_INFO_CHANGE_READY, NULL);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p info change ready failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
break;
}
} else {
char log_buf[256];
RK_S32 log_size = sizeof(log_buf) - 1;
RK_S32 log_len = 0;
RK_U32 err_info = mpp_frame_get_errinfo(frame);
RK_U32 discard = mpp_frame_get_discard(frame);
if (!data->first_frm)
data->first_frm = mpp_time();
log_len += snprintf(log_buf + log_len, log_size - log_len,
"decode get frame %d", data->frame_count);
if (mpp_frame_has_meta(frame)) {
MppMeta meta = mpp_frame_get_meta(frame);
RK_S32 temporal_id = 0;
mpp_meta_get_s32(meta, KEY_TEMPORAL_ID, &temporal_id);
log_len += snprintf(log_buf + log_len, log_size - log_len,
" tid %d", temporal_id);
}
if (err_info || discard) {
log_len += snprintf(log_buf + log_len, log_size - log_len,
" err %x discard %x", err_info, discard);
}
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p %s\n", ctx, log_buf);
data->frame_count++;
if (data->fp_output && !err_info)
dump_mpp_frame_to_file(frame, data->fp_output);
if (data->fp_verify) {
calc_frm_crc(frame, checkcrc);
write_frm_crc(data->fp_verify, checkcrc);
}
fps_calc_inc(cmd->fps);
}
frm_eos = mpp_frame_get_eos(frame);
mpp_frame_deinit(&frame);
get_frm = 1;
}
// try get runtime frame memory usage
if (data->frm_grp) {
size_t usage = mpp_buffer_group_usage(data->frm_grp);
if (usage > data->max_usage)
data->max_usage = usage;
}
// if last packet is send but last frame is not found continue
if (pkt_eos && pkt_done && !frm_eos) {
msleep(1);
continue;
}
if (frm_eos) {
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p found last packet\n", ctx);
break;
}
if ((data->frame_num > 0 && (data->frame_count >= data->frame_num)) ||
((data->frame_num == 0) && frm_eos))
break;
if (get_frm)
continue;
break;
} while (1);
if ((data->frame_num > 0 && (data->frame_count >= data->frame_num)) ||
((data->frame_num == 0) && frm_eos)) {
data->loop_end = 1;
break;
}
if (pkt_done)
break;
/*
* why sleep here:
* mpi->decode_put_packet will failed when packet in internal queue is
* full,waiting the package is consumed .Usually hardware decode one
* frame which resolution is 1080p needs 2 ms,so here we sleep 1ms
* * is enough.
*/
msleep(1);
} while (1);
return ret;
}
static int dec_advanced(MpiDecLoopData *data)
{
MPP_RET ret = MPP_OK;
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd = data->cmd;
MppCtx ctx = data->ctx;
MppApi *mpi = data->mpi;
MppPacket packet = NULL;
MppPacket packet_ret = NULL;
MppFrame frame = data->frame;
MppFrame frame_ret = NULL;
MppMeta meta = NULL;
RK_U32 quiet = data->quiet;
FileBufSlot *slot = NULL;
FrmCrc *checkcrc = &data->checkcrc;
ret = reader_index_read(cmd->reader, 0, &slot);
mpp_assert(ret == MPP_OK);
mpp_assert(slot);
mpp_packet_init_with_buffer(&packet, slot->buf);
// setup eos flag
if (slot->eos)
mpp_packet_set_eos(packet);
/* use the MppFrame with prealloced buffer and do not release */
meta = mpp_packet_get_meta(packet);
if (meta)
mpp_meta_set_frame(meta, KEY_OUTPUT_FRAME, frame);
ret = mpi->decode_put_packet(ctx, packet);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp decode put packet failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
data->loop_end = 1;
goto DONE;
}
if (!data->first_pkt)
data->first_pkt = mpp_time();
ret = mpi->decode_get_frame(ctx, &frame_ret);
if (ret || !frame_ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp decode get frame failed ret %d frame %p\n", ctx, ret, frame_ret);
data->loop_end = 1;
goto DONE;
}
if (!data->first_frm)
data->first_frm = mpp_time();
if (frame_ret != frame)
mpp_err_f("mismatch frame %p -> %p\n", frame_ret, frame);
/* write frame to file here */
if (data->fp_output)
dump_mpp_frame_to_file(frame_ret, data->fp_output);
if (data->fp_verify) {
calc_frm_crc(frame_ret, checkcrc);
write_frm_crc(data->fp_verify, checkcrc);
}
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p decoded frame %d\n", ctx, data->frame_count);
data->frame_count++;
if (mpp_frame_get_eos(frame_ret))
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p found eos frame\n", ctx);
fps_calc_inc(cmd->fps);
meta = mpp_frame_get_meta(frame);
if (meta) {
ret = mpp_meta_get_packet(meta, KEY_INPUT_PACKET, &packet_ret);
if (ret || !packet_ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp meta get packet failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
goto DONE;
}
if (packet_ret != packet)
mpp_err_f("mismatch packet %p -> %p\n", packet, packet_ret);
}
if (data->frame_num > 0) {
if (data->frame_count >= data->frame_num)
data->loop_end = 1;
} else if (data->frame_num == 0) {
if (slot->eos)
data->loop_end = 1;
}
DONE:
mpp_packet_deinit(&packet);
return ret;
}
void *thread_decode(void *arg)
{
MpiDecLoopData *data = (MpiDecLoopData *)arg;
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd = data->cmd;
MppCtx ctx = data->ctx;
MppApi *mpi = data->mpi;
RK_S64 t_s, t_e;
memset(&data->checkcrc, 0, sizeof(data->checkcrc));
data->checkcrc.luma.sum = mpp_malloc(RK_ULONG, 512);
data->checkcrc.chroma.sum = mpp_malloc(RK_ULONG, 512);
t_s = mpp_time();
if (cmd->simple) {
while (!data->loop_end)
dec_simple(data);
} else {
/* NOTE: change output format before jpeg decoding */
if (MPP_FRAME_FMT_IS_YUV(cmd->format) || MPP_FRAME_FMT_IS_RGB(cmd->format)) {
MPP_RET ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_OUTPUT_FORMAT, &cmd->format);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("Failed to set output format 0x%x\n", cmd->format);
return NULL;
}
}
while (!data->loop_end)
dec_advanced(data);
}
t_e = mpp_time();
data->elapsed_time = t_e - t_s;
data->frame_rate = (float)data->frame_count * 1000000 / data->elapsed_time;
data->delay = data->first_frm - data->first_pkt;
mpp_log("decode %d frames time %lld ms delay %3d ms fps %3.2f\n",
data->frame_count, (RK_S64)(data->elapsed_time / 1000),
(RK_S32)(data->delay / 1000), data->frame_rate);
MPP_FREE(data->checkcrc.luma.sum);
MPP_FREE(data->checkcrc.chroma.sum);
return NULL;
}
int dec_decode(MpiDecTestCmd *cmd)
{
// base flow context
MppCtx ctx = NULL;
MppApi *mpi = NULL;
// input / output
MppPacket packet = NULL;
MppFrame frame = NULL;
// paramter for resource malloc
RK_U32 width = cmd->width;
RK_U32 height = cmd->height;
MppCodingType type = cmd->type;
// config for runtime mode
MppDecCfg cfg = NULL;
RK_U32 need_split = 1;
// resources
MppBuffer frm_buf = NULL;
pthread_t thd;
pthread_attr_t attr;
MpiDecLoopData data;
MPP_RET ret = MPP_OK;
mpp_log("mpi_dec_test start\n");
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
cmd->simple = (cmd->type != MPP_VIDEO_CodingMJPEG) ? (1) : (0);
if (cmd->have_output) {
data.fp_output = fopen(cmd->file_output, "w+b");
if (NULL == data.fp_output) {
mpp_err("failed to open output file %s\n", cmd->file_output);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
}
if (cmd->file_slt) {
data.fp_verify = fopen(cmd->file_slt, "wt");
if (!data.fp_verify)
mpp_err("failed to open verify file %s\n", cmd->file_slt);
}
ret = dec_buf_mgr_init(&data.buf_mgr);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("dec_buf_mgr_init failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
if (cmd->simple) {
ret = mpp_packet_init(&packet, NULL, 0);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("mpp_packet_init failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
} else {
RK_U32 hor_stride = MPP_ALIGN(width, 16);
RK_U32 ver_stride = MPP_ALIGN(height, 16);
ret = mpp_frame_init(&frame); /* output frame */
if (ret) {
mpp_err("mpp_frame_init failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
data.frm_grp = dec_buf_mgr_setup(data.buf_mgr, hor_stride * ver_stride * 4, 4, cmd->buf_mode);
if (!data.frm_grp) {
mpp_err("failed to get buffer group for input frame ret %d\n", ret);
ret = MPP_NOK;
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
/*
* NOTE: For jpeg could have YUV420 and YUV422 the buffer should be
* larger for output. And the buffer dimension should align to 16.
* YUV420 buffer is 3/2 times of w*h.
* YUV422 buffer is 2 times of w*h.
* So create larger buffer with 2 times w*h.
*/
ret = mpp_buffer_get(data.frm_grp, &frm_buf, hor_stride * ver_stride * 4);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("failed to get buffer for input frame ret %d\n", ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
mpp_frame_set_buffer(frame, frm_buf);
}
// decoder demo
ret = mpp_create(&ctx, &mpi);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("mpp_create failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
mpp_log("%p mpi_dec_test decoder test start w %d h %d type %d\n",
ctx, width, height, type);
ret = mpp_init(ctx, MPP_CTX_DEC, type);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp_init failed\n", ctx);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
mpp_dec_cfg_init(&cfg);
/* get default config from decoder context */
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_GET_CFG, cfg);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p failed to get decoder cfg ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
/*
* split_parse is to enable mpp internal frame spliter when the input
* packet is not aplited into frames.
*/
ret = mpp_dec_cfg_set_u32(cfg, "base:split_parse", need_split);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p failed to set split_parse ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_CFG, cfg);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p failed to set cfg %p ret %d\n", ctx, cfg, ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
data.cmd = cmd;
data.ctx = ctx;
data.mpi = mpi;
data.loop_end = 0;
data.packet = packet;
data.frame = frame;
data.frame_count = 0;
data.frame_num = cmd->frame_num;
data.quiet = cmd->quiet;
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE);
ret = pthread_create(&thd, &attr, thread_decode, &data);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("failed to create thread for input ret %d\n", ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
if (cmd->frame_num < 0) {
// wait for input then quit decoding
mpp_log("*******************************************\n");
mpp_log("**** Press Enter to stop loop decoding ****\n");
mpp_log("*******************************************\n");
getc(stdin);
data.loop_end = 1;
}
pthread_join(thd, NULL);
cmd->max_usage = data.max_usage;
ret = mpi->reset(ctx);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpi->reset failed\n", ctx);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
MPP_TEST_OUT:
if (data.packet) {
mpp_packet_deinit(&data.packet);
data.packet = NULL;
}
if (frame) {
mpp_frame_deinit(&frame);
frame = NULL;
}
if (ctx) {
mpp_destroy(ctx);
ctx = NULL;
}
if (!cmd->simple) {
if (frm_buf) {
mpp_buffer_put(frm_buf);
frm_buf = NULL;
}
}
data.frm_grp = NULL;
if (data.buf_mgr) {
dec_buf_mgr_deinit(data.buf_mgr);
data.buf_mgr = NULL;
}
if (data.fp_output) {
fclose(data.fp_output);
data.fp_output = NULL;
}
if (data.fp_verify) {
fclose(data.fp_verify);
data.fp_verify = NULL;
}
if (cfg) {
mpp_dec_cfg_deinit(cfg);
cfg = NULL;
}
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
RK_S32 ret = 0;
MpiDecTestCmd cmd_ctx;
MpiDecTestCmd* cmd = &cmd_ctx;
memset((void*)cmd, 0, sizeof(*cmd));
cmd->format = MPP_FMT_BUTT;
cmd->pkt_size = MPI_DEC_STREAM_SIZE;
// parse the cmd option
ret = mpi_dec_test_cmd_init(cmd, argc, argv);
if (ret)
goto RET;
mpi_dec_test_cmd_options(cmd);
ret = dec_decode(cmd);
if (MPP_OK == ret)
mpp_log("test success max memory %.2f MB\n", cmd->max_usage / (float)(1 << 20));
else
mpp_err("test failed ret %d\n", ret);
RET:
mpi_dec_test_cmd_deinit(cmd);
return ret;
}
- compile
gcc mpp_dec_test.c -o mpp_dec_test `pkg-config --cflags --libs rockchip_mpp rockchip_vpu` -lutils
- run
tail -f /var/log/syslog //Open a new terminal and monitor the output
./mpp_dec_test -i /media/200frames_count.h264 -t 7 -n 200 -o ./decode.raw -w 640 -h 480
¶ QT
Use the following steps to install Qt
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt-get install qtbase5-dev qtchooser qt5-qmake qtbase5-dev-tools
sudo apt-get install qtcreator
sudo apt-get install qt5*
¶ Electron
- install Electron
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nodejs npm
npm install electron -D
- Project initialization
mkdir my-electron-app && cd my-electron-app
npm init
- Modify the packaging.json configuration file
vim package.json
{
"name": "my-electron-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "main.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "electron ."
},
"author": "9527",
"license": "ISC",
"description": "electron test",
"dependencies": {
"electron": "^31.2.0"
}
}
- Create main.js
vim main.js
console.log(123)
- run
npm start
¶ NPU
¶ Introduction
RK3588 has a built-in NPU module, with a processing performance of up to 6TOPS. To use this NPU, you need to download the RKNN SDK. The RKNN SDK includes two sets of source code, one is RKNN-Toolkit2, which is used to convert onnx models into rknn models. The other set is RKNPU2. It is used for inference at the board end. Below are two sets of source code introduced separately.
¶ PC Model Conversion and Reasoning RKNN-Toolkit2
There are two methods to install RKNN-Toolkit2: through 'pip install' or through Docker image installation.
- Open a terminal command line window and install Python 3.6 and pip3
sudo apt-get install python3 python3-dev python3-pip
- Install the required dependency packages.
sudo apt-get install libxslt1-dev zlib1g-dev libglib2.0 libsm6 libgl1-mesa-glx libprotobuf-dev gcc
- Download the RKNN-Toolkit2 tool
git clone https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-toolkit2.git
cd rknn-toolkit2
- Install necessary corresponding versions of dependency packages.
pip3 install -r doc/requirements_cp36-1.5.2.txt
- install RKNN-Toolkit2(Python3.8 for x86_64)。
pip3 install packages/rknn_toolkit2-1.5.2+b642f30c-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
The currently installed onnx will be the latest version 1.19.1, which will report an error: AttributeError: module 'onnx' has no attribute 'mapping'
pip3 install onnx==1.18.0 onnxruntime==1.18.0
- Check if RKNN-Toolkit2 has been successfully installed.
# If no errors occur, it means the installation was successful. Simultaneously hold down Ctrl+D to exit Python3.
python3
from rknn.api import RKNN
- Convert yolov5s_relu.onnx to rknn model and run the model inference image
cd examples/onnx/yolov5
python3 test.py
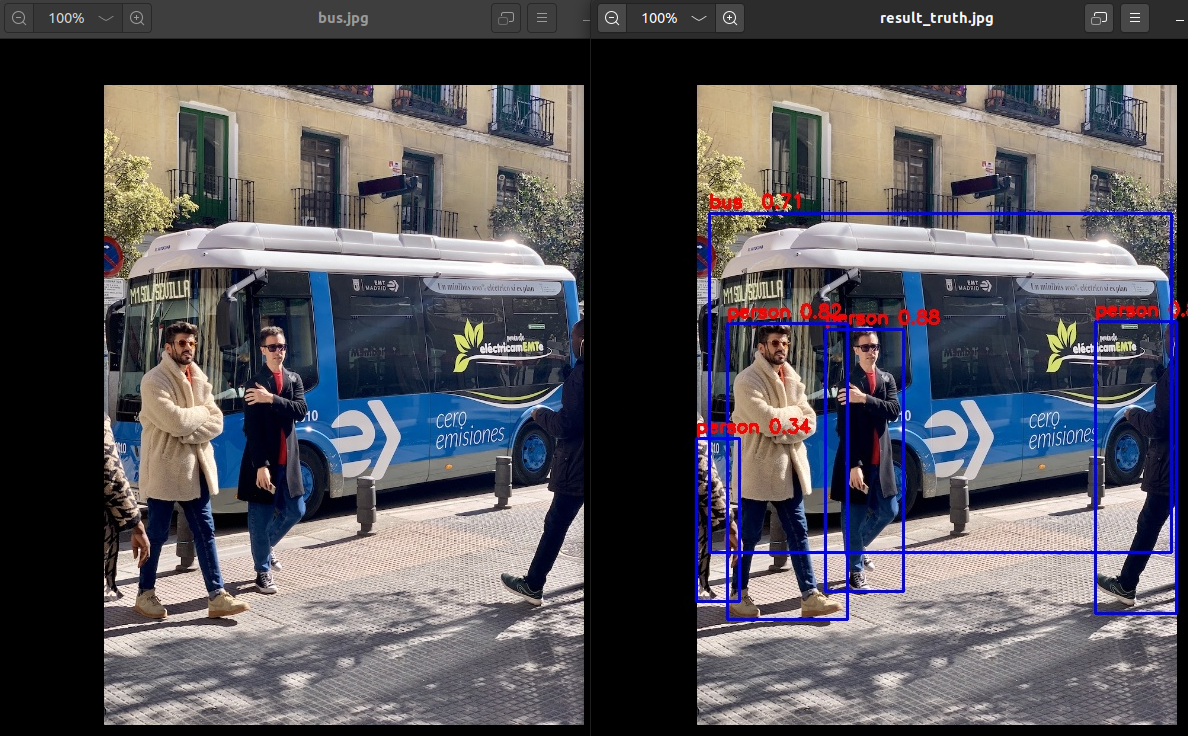
After successfully running the conversion model and inference script test. py, the default save path for the converted model is' examples/onnx/yolov5/yolov5s_relu. rknn ', and the inference image results are saved in examples/onnx/yolov5/result.jpg 。
- Install the Docker environment.
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
sudo apt update
apt-cache policy docker-ce
sudo apt install docker-ce
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo reboot
sudo systemctl status docker
- Download the RKNN-Toolkit2 tool
git clone https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-toolkit2.git
cd rknn-toolkit2
- Run
Docker
cd docker/docker_full/
# Load image
docker load --input rknn-toolkit2-1.5.2-cp36-docker.tar.gz
# If REPOSITORY is rknn-toolkit2 and TAG is 1.x.x-cp36, it indicates successful loading.
docker images
# Run the Docker container, where~/share/test/rknn toolkit2-1.5.2/examples/onnx/yolov5 is the author's path, and readers need to modify it to their own path.
docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb -v ~/share/test/rknn-toolkit2-1.5.2/examples/onnx/yolov5:/rknn_yolov5_demo rknn-toolkit2:1.5.2-cp36 /bin/bash
cd rknn_yolov5_demo
# Convert yolov5s_relu.onnx to the rknn model for parallel inference of images.
python3 ./test.py
# exit Docker
exit
After successfully running the conversion model and inference script test. py, the default save path for the converted model is' examples/onnx/yolov5/yolov5s_relu. rknn ', and the inference image results are saved in' examples/onnx/yolov5/result. jpg '.

¶ PC connection board end inference
The first two methods of conversion and inference models both run in the PC simulator environment. This paragraph modifies the inference environment to board end inference based on the above two methods.
- The author's PC is built using a virtual machine called the 'Ubuntu' system. The 'ADB' command needs to be installed. If the reader's PC is on a different system, please search online for ways to install adb.
sudo apt install adb
Connect the 'type-c' port of the development board to the 'USB' port of the computer, and enter the following command in the 'Ubuntu system' on the PC side to check if it is properly connected to the development board.
adb shell
exit
- Check if the rknn service on the development board is running.
adb shell pgrep rknn_server
If there is no process number output, it means that the rknn service is not running. You need to enter one of the following commands.
adb shell
# Restart rknn service
restart_rknn.sh
# Or start the rknn service
start_rknn.sh
exit
- Check the adb device ID number of the development board
adb devices
The ID number of the author's development board adb here is ca32be3b402e6579.
- Modify the test. py script
open rknn-toolkit2/examples/onnx/yolov5/test.py
# Modify the script target and device id. Modify the corresponding platform type values ("rk3566", "rk3568", "rk3588", "rv1103", "rv1106", "rk3562") and device IDs, save them, and then execute the script to generate a model suitable for the board and perform inference on the image.
# Find the following statement
rknn.config(mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]], std_values=[[255, 255, 255]], target_platform='rk3566')
...
ret = rknn.init_runtime()
# modify to
rknn.config(mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]], std_values=[[255, 255, 255]], target_platform='rk3588')
...
ret = rknn.init_runtime(target='rk3588', device_id='ca32be3b402e6579')