¶ SPI interface development(Linux)
Hardware interface description:
JSPI interface on motherboard, socket wire sequence description:
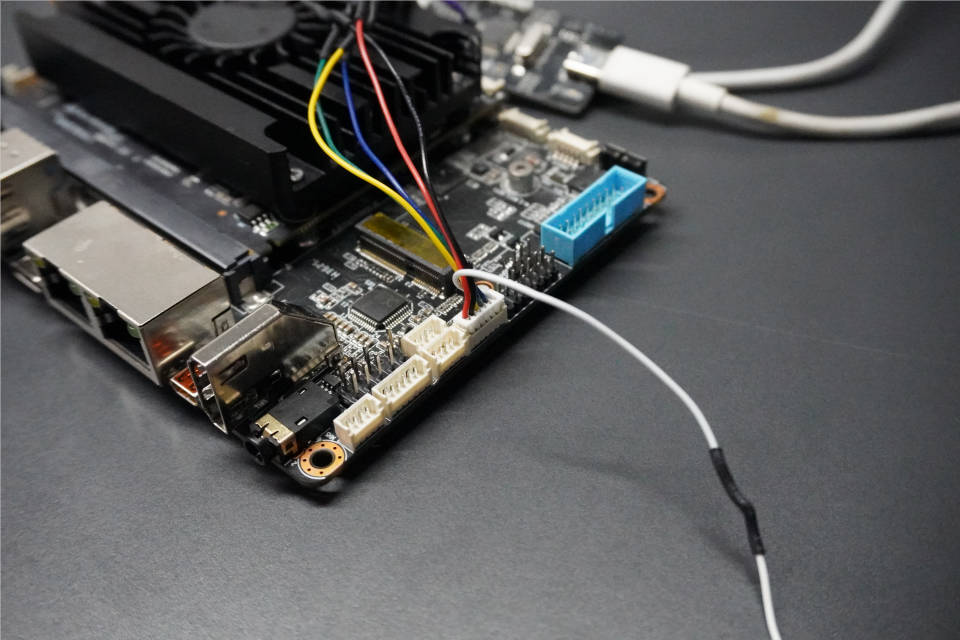
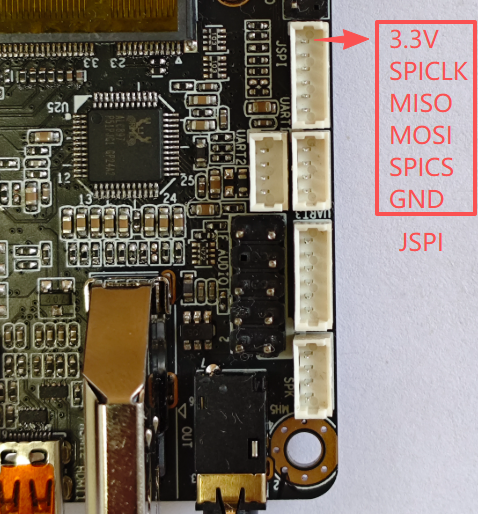
| Serial Number | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V | 3.3V power supply |
| 2 | SPICLK | SPI clock |
| 3 | SPIMISO | |
| 4 | SPIMOSI | |
| 5 | SPICS | Film Selection |
| 6 | GND | Power ground |
¶ Section 1: SPI Basic Knowledge
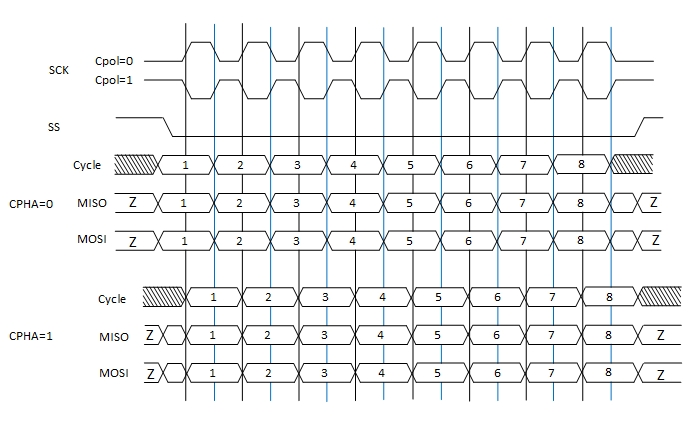
1.1 SPI has four modes, as follows:
The different combinations of CPOL (clock polarity) and CPHA (clock phase) form different modes of the SPI bus. Different SPI slave devices support different modes
| Mode | CPOL | CPHA |
|---|---|---|
| Mode 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Mode 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Mode 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Mode 4 | 1 | 1 |
1.2 Sample timing chart
¶ Section 2: Method of Adding SPI Nodes to Linux
Taking Ubuntu 22.04.x-desktop-amd64 version as an example,
Enter the following commands in sequence to add the SPI node
These commands are temporary additions to SPI nodes and need to be added during program startup so that SPI can be used normally later on
jb@K1:~$ sudo modprobe spidev
jb@K1:~$ echo spidev | sudo tee /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi-SPI1001:00/driver_override
jb@K1:~$ echo spi-SPI1001:00 | sudo tee /sys/bus/spi/drivers/spidev/bind
jb@K1:~$ sudo chmod 666 /dev/spidev0.0
jb@K1:~$ ls /dev/spi*
/dev/spidev0.0
Add SPI node to download ready-made script: mkspi.sh to execute with sudo privileges:
http://dd.youyeetoo.cn:5000/sharing/RYIHfvSjp
¶ Section 3: Testing Linux SPI
Download the Linux spi testing software source code
linux-SPI-test-src-File
After decompression, enter the Linux spi folder,
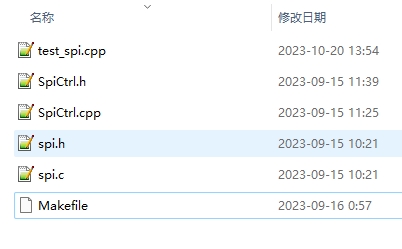
Source code directory structure description:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| SPI. h | SPI underlying operation encapsulation |
| SPI. c | SPI underlying operation encapsulation |
| SpiCtrl. h | SPI application interface header file |
| SpiCtrl. cpp | SPI application interface source file |
| Test_ Spi. cpp | Test code main |
| Makefile | Make Compilation Script File |
Need to download basic compilation tools, refer to the description of "Linux application development (calling hardware)"
Compile and run the test program as follows:
#Compilation
jb@K1:~/linx-spi$ make
#Execution
jb@K1:~/linx-spi$ sudo ./test_spi
If there are no errors in the above process, the result of executing the program is as follows;
$ sudo ./test_spi
If Spi Is Enabled The Read And Write Operations Will Be Synchronized
SPI_FullDuplex Success,Read The Contents:FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
bye
Interface File SpiCtrl. h Description
#ifndef _SPI_CTRL_H
#define _SPI_CTRL_H
#include <stdint.h>
#include "spi.h"
class SpiCtrl
{
private:
spi_t *spi;
public:
SpiCtrl();
~SpiCtrl();
public:
/**
*@ brief: Open the connection to the SPI bus
*@ param {char} * path: spi Bus path:/dev/spix
*@ param {unsigned int} mode: mode: 0,1,2,3
*@ param {uint32_t} max_ Speed: rate
*@ return {*} returns 0 success, other failures
**/
int32_t Open(const char *path, unsigned int mode,uint32_t max_speed);
/**
*@ brief: Open the connection SPI bus advanced method
*@ param {char} * path: spi Bus path:/dev/spix
*@ param {unsigned int} mode: mode: 0,1,2,3
*@ param {uint32_t} max_ Speed: rate
*@ param {spi_bit_order_t} bit_ Order: Large end small end MSB_ FIRST, LSB_ FIRST
*@ param {uint8_t} bits_ Per_ Word: Set the word length for SPI communication
*Param {uint8_t} extra_ Flags: extended parameters
*@ return {*} returns 0 success, other failures
**/
int32_t open_advanced(const char *path, unsigned int mode,uint32_t max_speed, spi_bit_order_t bit_order,uint8_t bits_per_word, uint8_t extra_flags);
/**
*@ brief: Release SPI bus
*@ return {*}
**/
void Release();
/**
* @brief : Is the SPI bus on
* @return {*}
**/
bool isOpen();
/**
*@ brief: SPI writes data first and then reads data
*@ param {uint8_t} * lpWriteBuf: data memory to be written
*@ param {int32_t} WriteBuf_ Len: data length
*@ param {uint8_t} * lpReadBuf: data memory to be read
*@ param {int32_t} ReadBuf_ Len: data length
*@ return {*} returns 0 success, other failures
**/
int32_t SPI_WriteRead( uint8_t *lpWriteBuf, int32_t WriteBuf_len, uint8_t *lpReadBuf, int32_t ReadBuf_len);
/**
*@brief:SPI仅写
*@param{uint8_t}*lpWriteBuffer:data memory to be written
*@param{int32_t}WriteLength:data length
*@return{*}returns 0 success, other failures
**/
int32_t SPI_Write( uint8_t *lpWriteBuffer, int32_t WriteLength);
/**
*@ brief: SPI synchronous write read
*@ param {uint8_t} * lpWriteBuf: data memory to be written
*@ param {uint8_t} * lpReadBuf: Read data memory to be synchronized
*@ param {int32_t} len: Data length
*@ return {*} returns 0 success, other failures
**/
int32_t SPI_FullDuplex( uint8_t *lpWriteBuf, uint8_t *lpReadBuf, int32_t len);
};
#endif
¶ Section 4: SPI Test Program Qt Interface
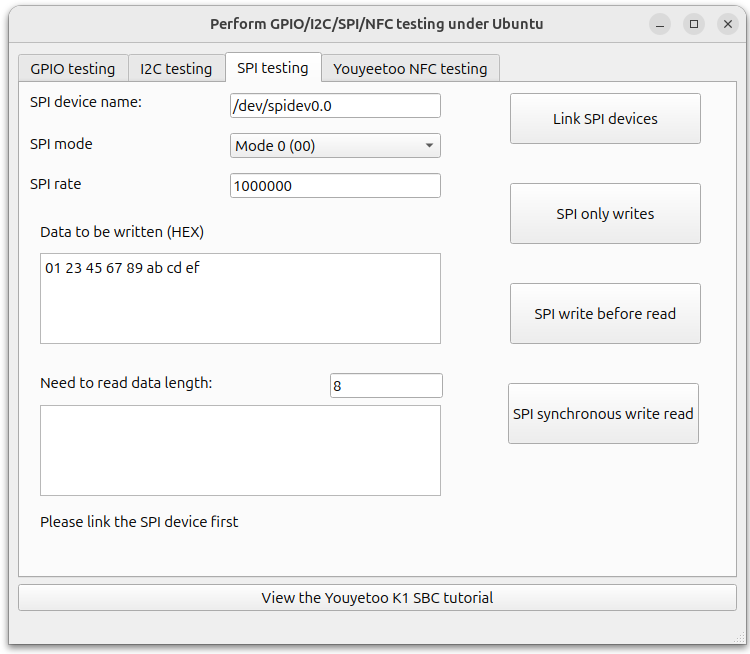
Operation process:
- Select mode, rate, and then 'Connect SPI device'
- Action:
SPI Write Only ": Write only but not read, this operation needs to be selected based on the communication timing of the slave device
SPI write first read later ": Write data to the slave device first, and then read data. This operation needs to be selected based on the communication timing of the slave device
SPI synchronous write read ": Write data to the slave device while reading data from the device. This operation needs to be selected based on the communication timing of the slave device
Please refer to the following page for sample source code and how to compile and use the QT interface of the testing program:
https://wiki.youyeetoo.com/en/youyeetooK1/linux/qt-build