¶ 1 Introduction
This page introduces
CAN
¶ 2 Viewing Nodes
- Querying Current Network Devices
$ ifconfig -a
can0: flags=128<NOARP> mtu 16
unspec 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 txqueuelen 10 (UNSPEC)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device interrupt 71
......
- Starting CAN:
# Stopping CAN:
$ ip link set can0 down
# Set bitrate to 500kHz:
$ ip link set can0 type can bitrate 500000
# Print can0 information:
$ ip -details -statistics link show can0
# Start CAN:
$ ip link set can0 up
- CAN Transmit:
# Send standard frame, data frame
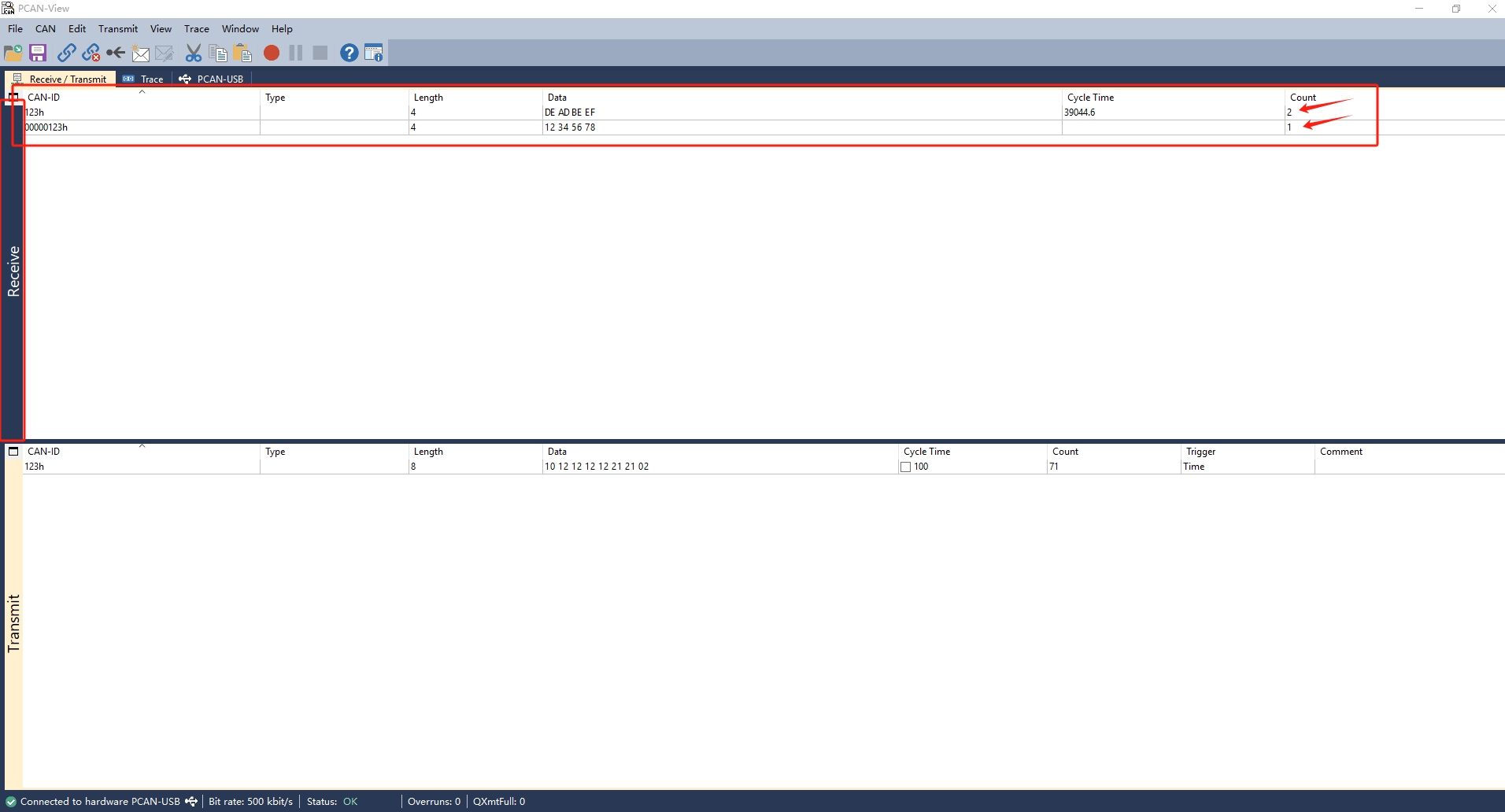
$ cansend can0 123#DEADBEEF
# Send standard frame, remote frame
$ cansend can0 123#R
# Send extended frame, data frame
$ cansend can0 00000123#12345678
# Send extended frame, remote frame
$ cansend can0 00000123#R
- CAN Receive:
$ candump can0
¶ 3 CAN Communication
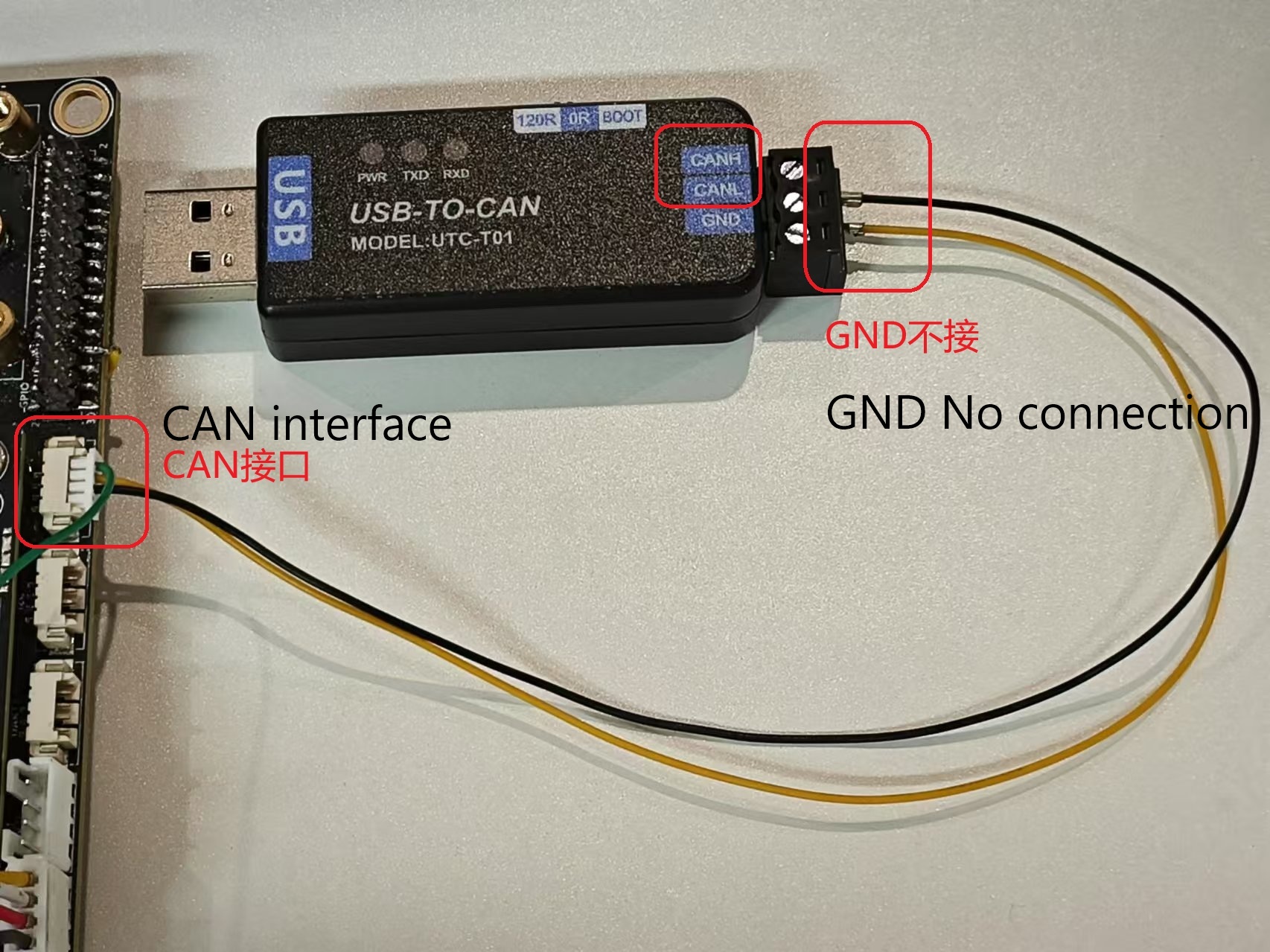
¶ 3.1 Hardware Connection
The specific module used by the reader shall prevail.
- One end of the USB is connected to the PC.
¶ 3.2 Sending and Receiving
¶ 3.2.1 youyeetooRJ Receiving Data
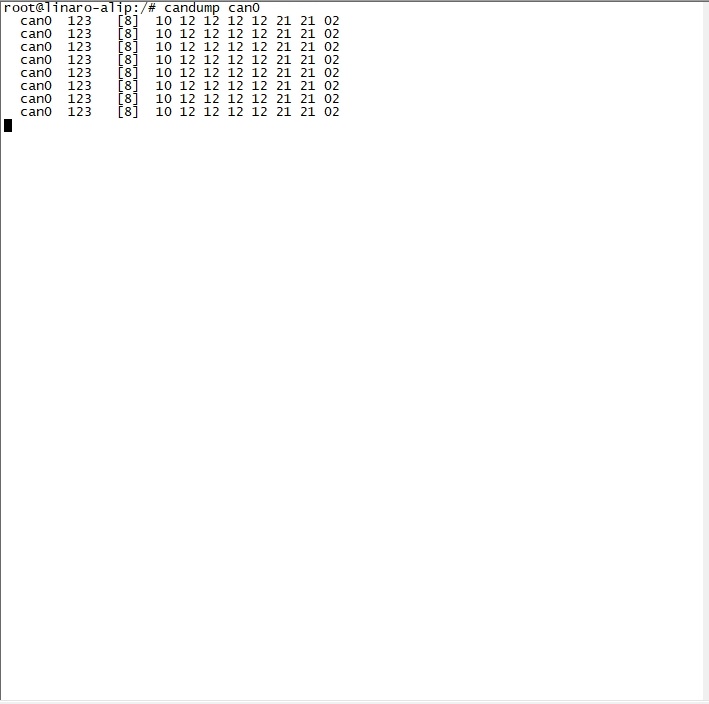
- Board-side Reception
$ candump can0
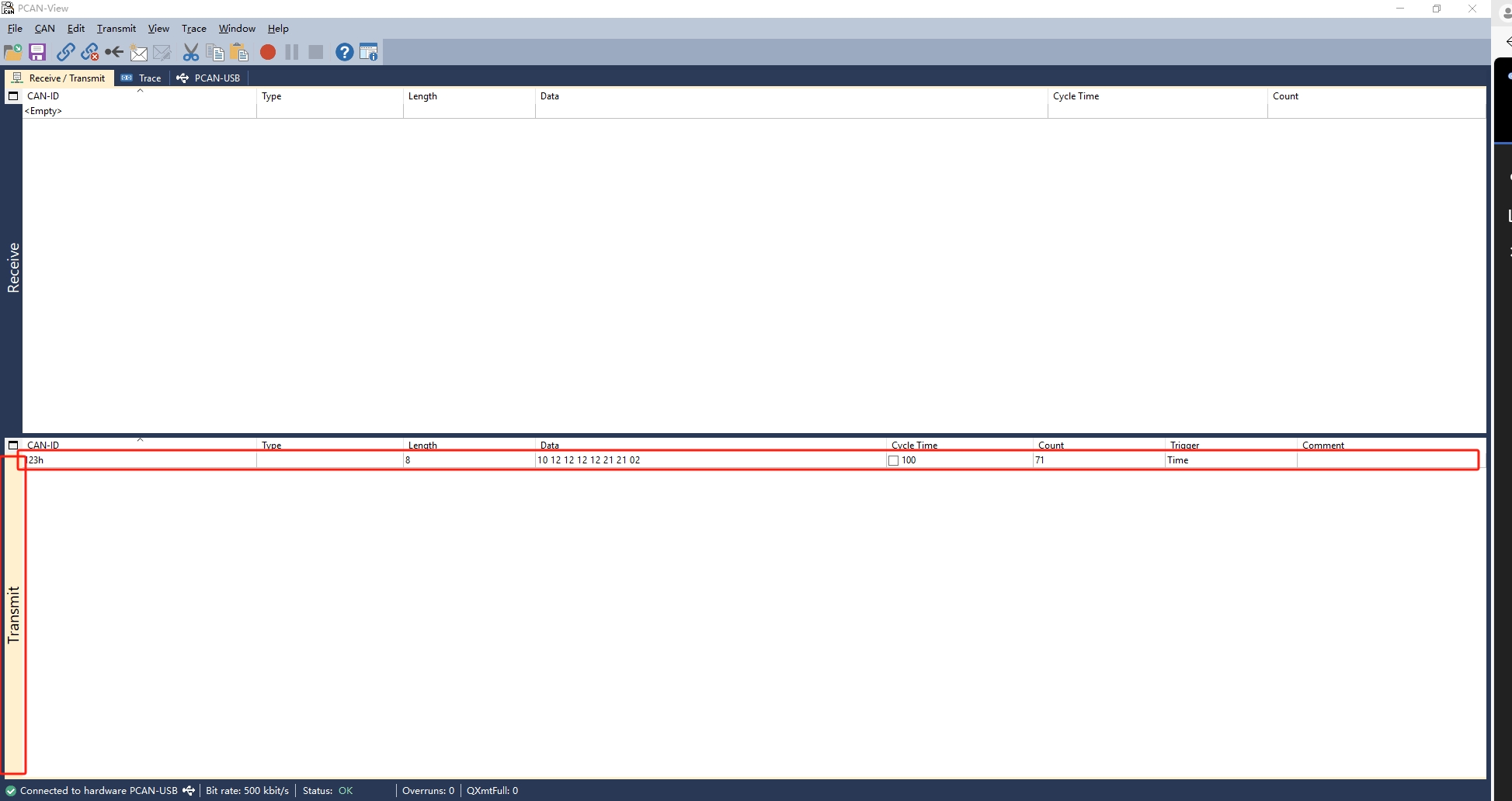
- PC-side Sending
¶ 3.2.2 youyeetooRJ Sending Data
- Board-side Sending
# Send standard frame, data frame
$ cansend can0 123#DEADBEEF
# Send standard frame, remote frame (Demo module does not support remote frames, not demonstrated here)
$ cansend can0 123#R
# Send extended frame, data frame
$ cansend can0 00000123#12345678
# Send extended frame, remote frame
$ cansend can0 00000123#R
- PC receiving